FIG 5.
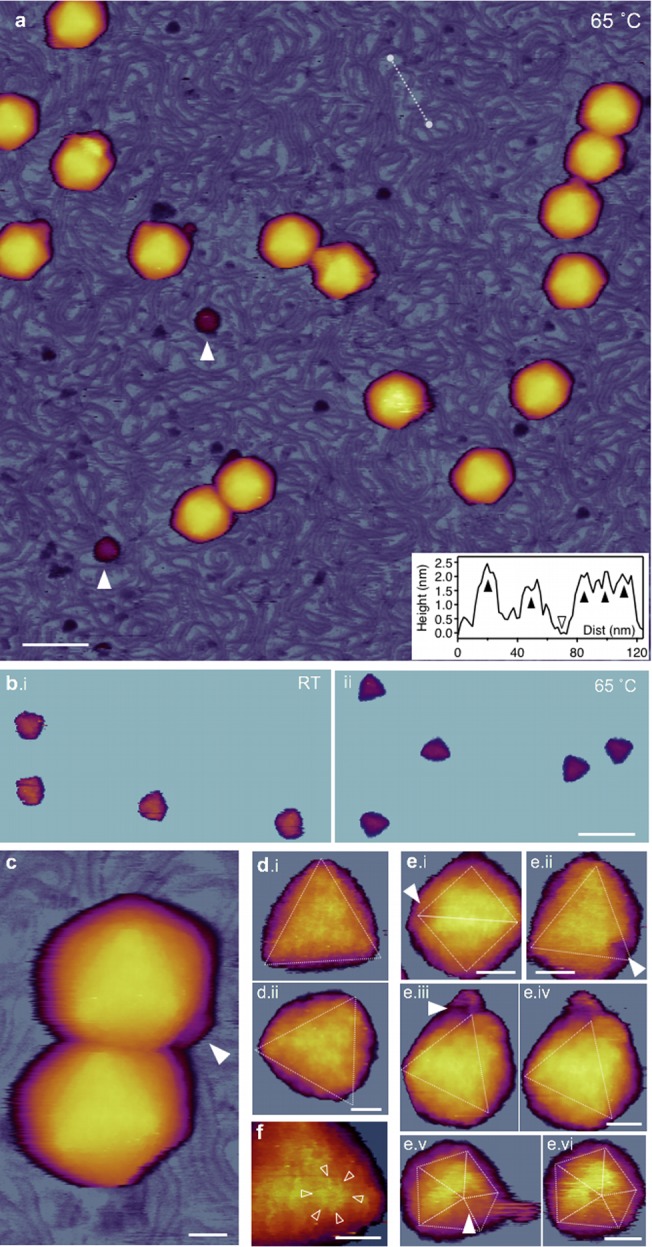
AFM of T7 phages treated at 65°C. (a) Overview of a 1-μm by 1-μm sample area. White arrowheads point at large (>10 nm) globular particles. Scale bar, 100 nm. (Inset) Topographical height map along an arbitrarily chosen line in the background (white dashed line). Black arrowheads point at DNA cross sections, whereas the empty arrowhead at the substrate (mica) surface. (b) Comparison of icosahedral facets of room temperature (i) and 65-degree (ii) capsids. AFM images were contrast enhanced with identical color-scale offset (48 nm) and range (20 nm). (c) AFM image of two T7 particles. The white arrowhead points at the short, stubby tail complex visible on one of the particles, whereas there is no visible tail on the other one. Scale bar, 20 nm. (d) High-resolution AFM images of 65°C-treated T7 phage particles with resolvable capsomeres on their surfaces. Views are along the 3-fold symmetry axes. Because of contrast enhancement, only the top facets are visible and the rest of the capsid is hidden. Scale bar, 10 nm. (e) T7 particles with resolvable DNA exit holes (white arrowheads). The exit hole appears as a gap in the location of a missing pentagonal capsomere at one of the icosahedron vertices. Images viewed along the 2-fold (i), 3-fold (ii, iii, and iv), and 5-fold (v and vi) symmetry axes are shown. Images iii and v are reconstructed from the rightward fast AFM scanlines, whereas images iv and vi are from leftward (reverse) scanlines from the same sample area. Scale bars, 20 nm. (f) Magnified view of a cogwheel-shaped hexagonal capsomere. Arrowheads point at the spokes of the cogwheel. Scale bar, 10 nm.
