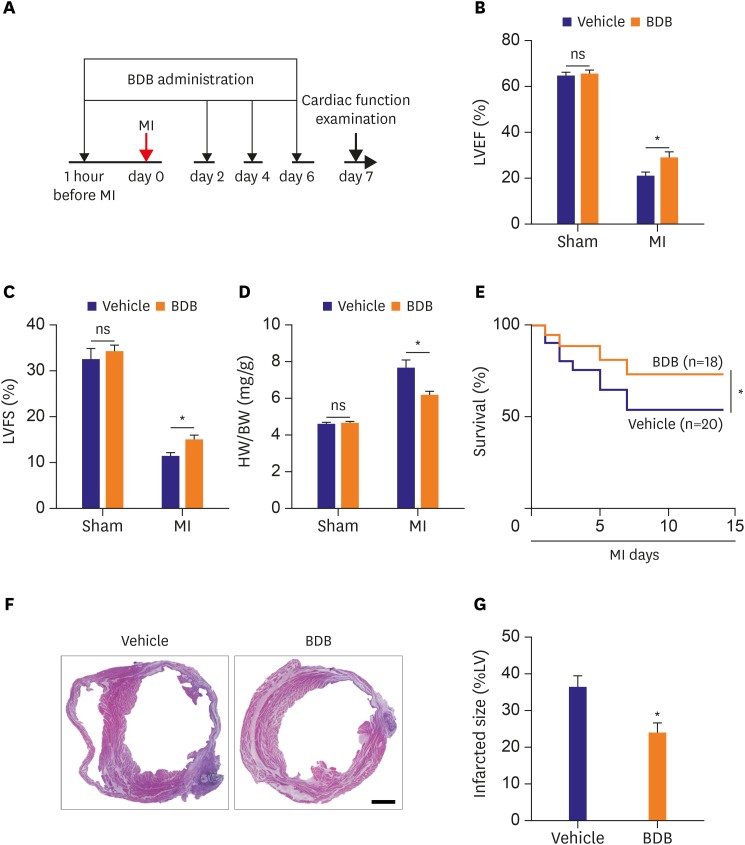
Figure 1. BDB treatment improved cardiac recovery after MI in mice. (A) Schematic of protocol for adoptive transfer and administration of BDB to mice. Acute MI was induced by surgical ligation of LAD in mice. (B, C) Cardiac function of vehicle and BDB treatment mice on day 14 after MI. (D) Ratio of HW/BW of mice was measured 14 days after MI. (E) Survival rates after MI in BDB- or vehicle-treated mice. Survival curves up to 2 weeks after MI were created by Kaplan-Meier method and compared by a log-rank test. (F) Representative H&E staining of heart sections from vehicle or BDB treated-mice at 2 weeks after MI (scale bar=1,000 μm). (G) Quantitative analysis of infarct size in vehicle and BDB treated-mice at 2 weeks after MI. Data are expressed as mean±SEM (n=6–14).
BDB = 3-Bromo-4,5-dihydroxybenzaldehyde; H&E = hematoxylin and eosin; HW/BW = heart weight to body weight; LAD = left anterior descending artery; LV = left ventricle; LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction; LVFS = left ventricular fractional shortening; MI = myocardial infarction; SEM = standard error of measurement.
*The p<0.05 compared with vehicle group.