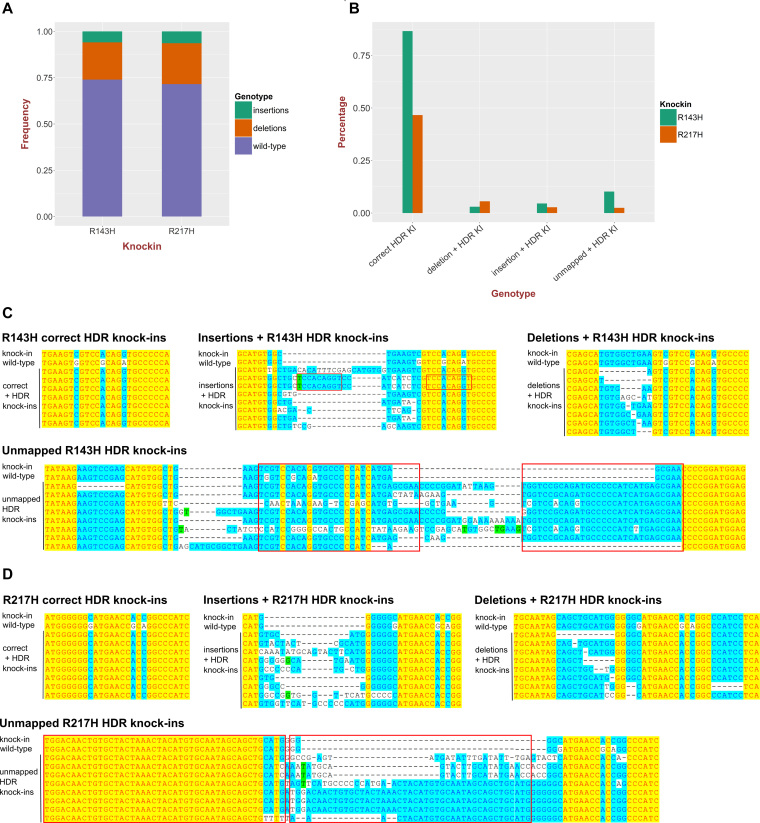
Figure 2.
High-throughput sequencing analysis of point mutation knock-ins into the tp53 gene. (A) Quantification of the total fractions of small insertions and deletions in tp53 R143H and R217H knock-in injected embryo samples. The proportion of the reads with deletions or insertions represents a measure of sgRNA activity. (B) Measurements of R143H and R217H correct HDR knock-ins, knock-ins with additional insertions and deletions as well as knock-in reads with more aberrant complex events (unmapped). (C) Examples of different classes of R143H knock-ins: correct HDR knock-ins, knock-ins with deletions or insertions and unmapped knock-ins aligned to WT and expected knock-in sequences. (D) Examples of different classes of R217H knock-ins: correct HDR knock-ins, knock-ins with deletions or insertions and unmapped knock-ins aligned to WT and expected knock-in sequences.