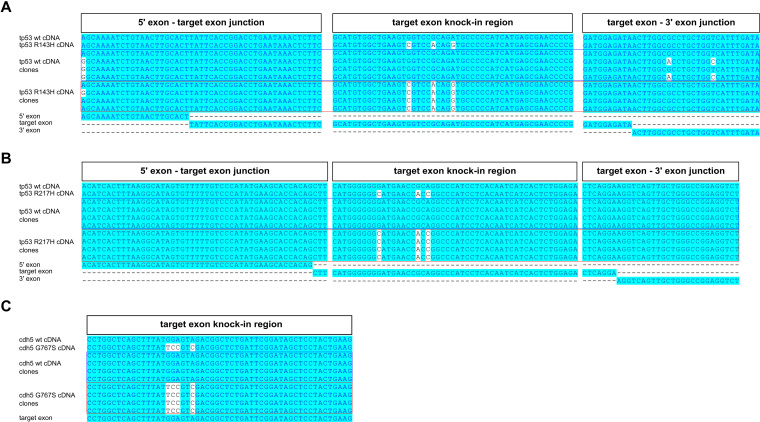
Figure 5.
Knock-in analysis of cDNAs isolated from F1 carrier zebrafish. Analysis of cDNA cloned from F1 knock-in zebrafish with introduced tp53 R143H (A), tp53 R217H (B) or cdh5 G767S (C) mutations was performed by cloning cDNA fragments, identifying bacterial clones carrying either WT cDNA plasmids or those with knock-in mutations introduced, sequencing them and aligning the reads to the expected WT and knock-in cDNA sequences. Each of the alignments was performed with WT and mutant cDNA reference sequences, four WT cDNA clones, four knock-in cDNA clones and relevant exons. For the tp53 R143H and R217H knock-ins (A and B) we show the junction of the 5′ exon and target exon, knock-in region in the target exon and the junction between the target exon and 3′ exon. For the cdh5 G767S knock-in, we only show the target exon alignment because the mutation is at the end of the last exon and therefore unlikely to affect splicing (C).