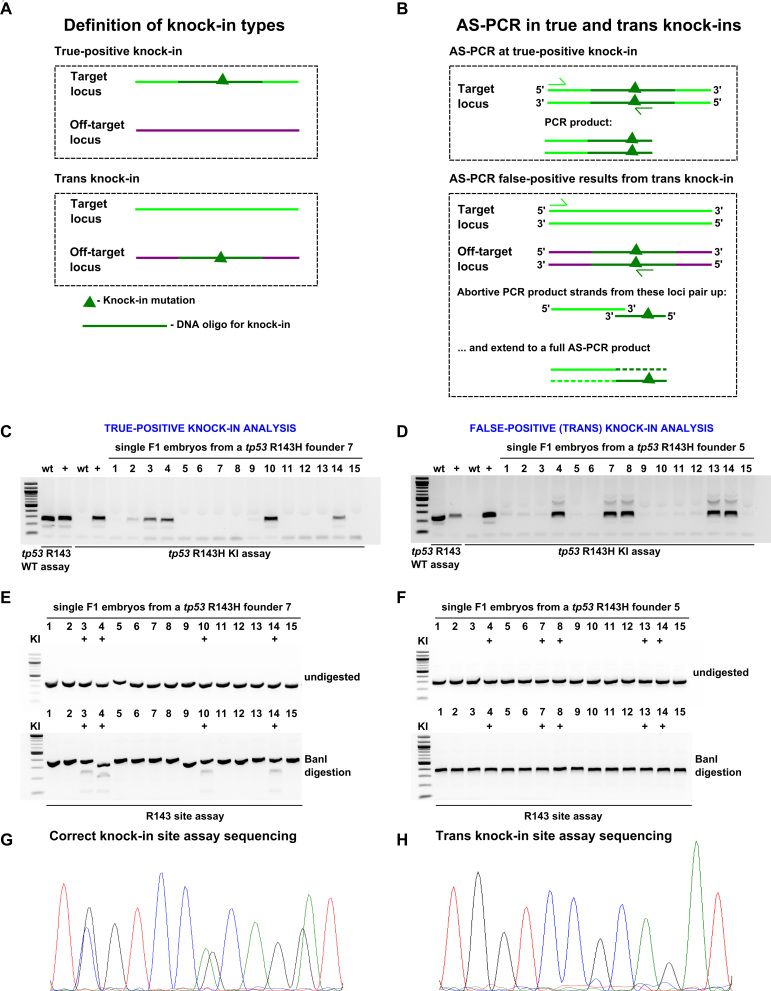
Figure 6.
Analysis of true and off-target (trans) knock-ins at tp53 R143H site. (A) Definitions of knock-in types. In true-positive knock-ins, the targeting oligo modifies the intended locus without off-target insertions, whereas in the trans knock-ins, insertion of the oligo occurs at an off-target locus. (B) A model of how AS-PCR can produce PCR products in both true-positive and trans knock-in situations. In the case of a true-positive knock-in case, standard PCR successfully amplifies the expected PCR product. A possible mechanism in the trans knock-in case is presented here involving an abortive PCR product strands from the WT intended knock-in locus and the trans knock-in off-target locus. Since the oligo and WT locus share significant homology, it is conceivable that very short abortive PCR products from the two loci can pair up and become amplified to the full PCR product in the next cycle thus initiating the exponential cycle of amplification leading to large amounts of PCR product visible as an apparent knock-in band. Screening and sequencing verification of true-positive (C, E and G) and trans (D, F and H) knock-ins. (C and D) A set of 15 F1 embryos from positive founders were analysed using tp53 R143H knock-in AS-PCR. WT and positive control samples were run with both the WT and knock-in PCRs as controls for the size of the PCR product and specificity of the assay. (E and F) Knock-in site assay PCRs were run on samples from both founders and then either run undigested (upper panel) or digested with BanI enzyme (lower panel) to detect the BanI site expected to be introduced by correct tp53 R143H mutation knock-in. The samples previously identified as positive for knock-in are marked with ‘+’. (G and H) R143H site assay sequencing for true-positive and trans knock-in samples. Chromatograms show that in the true-positive knock-in base positions, there are double peaks (G), which are absent from the comparable trans knock-in read (H).