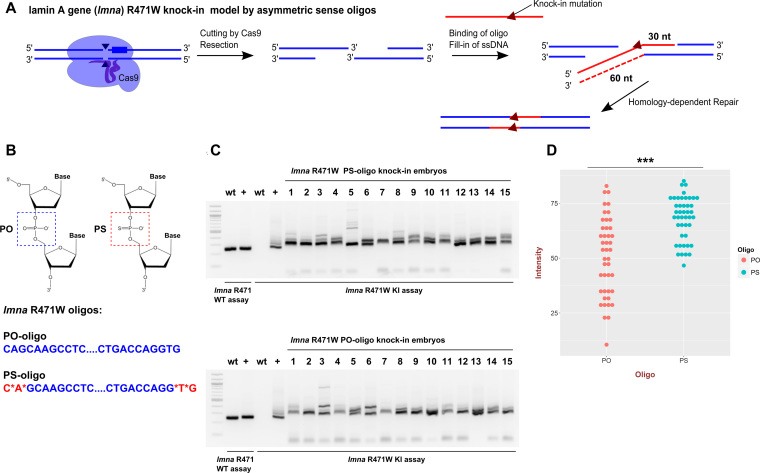
Figure 7.
PS-modified oligos improve knock-in consistency and efficiency. (A) Targeting scheme for introducing R471W knock-in into lamin A/C gene (lmna) in zebrafish using a sense asymmetric oligo. Red-colored lines indicate the donor oligo or DNA-derived from it and blue lines indicate genomic DNA. (B) Chemical structures of the PO and the PS groups show that one of the oxygens in PO is substituted with a sulphur atom in PS. The PS groups were added in the last two chemical bonds on either end of the PS-oligo for lmna R471W knock-in and the PO-oligo was synthesized in a standard way. (C) An example of gel data for AS-PCR analysis of lmna R471W knock-ins using PS and PO oligos. WT assay serves as a control for size of the products and the knock-in assay detects the modification. (D) Graph of measured intensities of AS-PCR signals for 44 embryos for each of the PO- and PS-oligo knock-in injected groups derived from three independent experiments. The data are aggregated because there was little variation between experiments. The type of oligo is indicated by color and with x-axis label. The ‘***’ indicate the P-value in t-test of < 0.001 (3.9e-07).