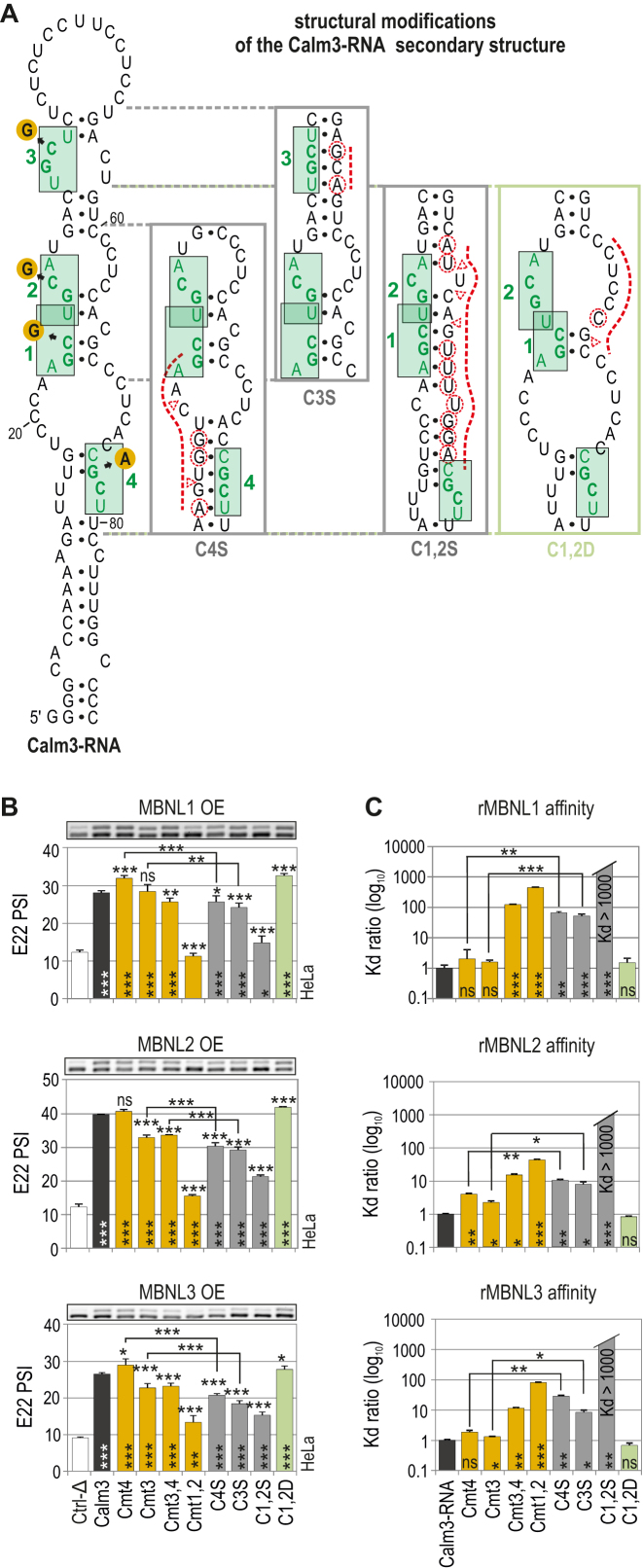
Figure 5.
Natural RNA structural determinants that modulate MBNL activity. (A) A secondary structure of Calm3-RNA containing MBNL1-binding motifs (HGCH – H stands for U, C or A) marked in green and numbered. Point mutations within the motifs are marked with orange circles. The structural modifications of particular Calm3-RNA regions are presented in boxes. Substitutions and insertions or deletions are marked with red dashed circles or triangles, respectively. (B) RT-PCR results showing the splicing response of pre-mRNAs of hybrid minigenes with incorporated different Calm3 regulatory elements carrying HGCH mutations or structural modifications upon MBNL1, MBNL2 and MBNL3 OE in HeLa cells. The MBNL paralogs are identical with respect to splicing isoforms (lacking residues encoded by alternative exons 5 and 7); n = 2. Vertical and horizontal asterisks denote the statistical significance of results in comparison to Ctrl-Δ and Calm3 WT constructs, respectively. Ctrl-Δ, Atp2a1-Δ minigene. (C) Quantification of the biochemical assay showing binding affinity of recombinant rMBNL1, rMBNL2 and rMBNL3 to intact Calm3-RNA, HGCH motif and RNA secondary structure mutants normalized to Calm3-RNA WT; n = 2–4 for each protein concentration (in the range of 0–200 nM of rMBNL1). Vertical asterisks denote the statistical significance of results in comparison to intact Calm3-RNA.