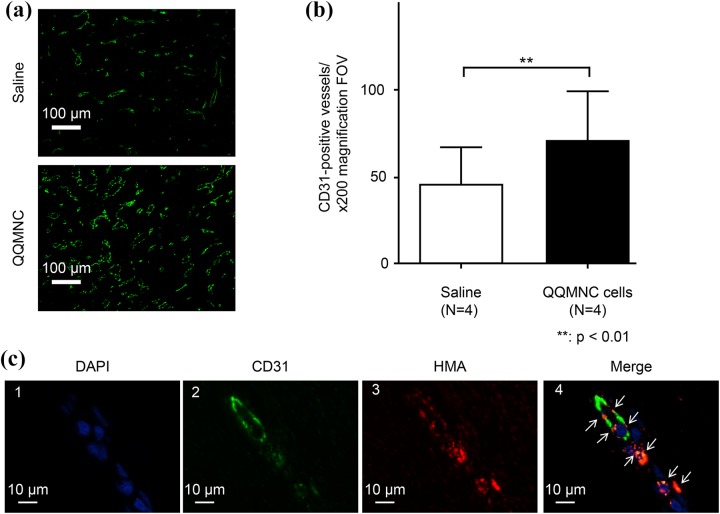
Figure 6.
Visualization and quantitation of capillaries in QQMNC-treated and control wounds by staining with the anti-CD31 antibody. (a) Representative microphotograph of granulation tissue in wound sections of control (top) and QQMNC-treated (bottom) wounds stained with the anti-CD31 antibody; 200× magnification. (b) Quantification of the number of capillaries. Significantly more CD31-positive vessels were present in QQMNC-treated wounds compared with saline-injected wounds. Each bar represents mean ± SD, saline n = 4, QQMNC n = 4, 200× magnification FOV. (c) Assessment of inclusion of human cells into newly formed capillaries in the muscular layer 1 cm from the edge of wounds injected with PKH26-QQMNC. 1: DAPI staining. 2: CD31 staining. Endothelial cells are stained in green. 3: Human mitochondria staining. The PKH26-QQMNC red signal is enhanced by HMA staining. 4: Merged microphotographs 1, 2, and 3. White arrows point to overlapping CD31 and HMA staining (orange) suggesting that QQMNC differentiated into endothelial cells.