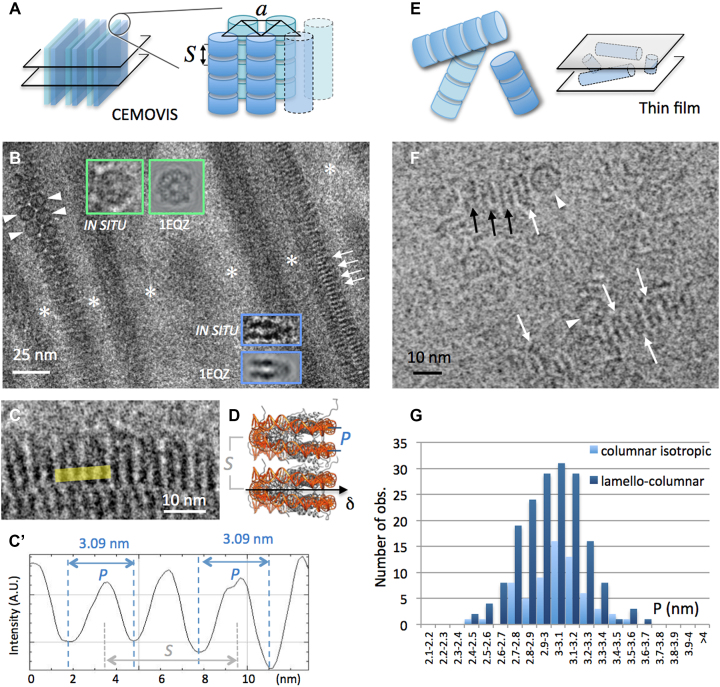
Figure 1.
CryoEM of NCP forming columnar phases in low salt solutions (15 mM [+]). (A) The lamello-columnar phase is composed of stacks of nucleosomes (columns) that align in parallel into a triangular lattice of parameter a, forming bilayers. Bulk phase (long range ordered bilayers) can be sectioned (e.g. transversally, left) and analysed by CEMOVIS. (B and C) CEMOVIS imaging of the lamello-columnar phase. Bilayers in transverse section are separated by particle-free layers of solvent (white stars). Columns of nucleosomes are seen in top (arrowheads), side (arrows) or oblique views. Top and side views are compared to the corresponding projections of the crystallographic structure of the NCP (from PDB ID: 1EQZ) in the inserts. (C and C’) Measurement of P-values on columns in side view. (D) In the columns of the lamello-columnar phase, nucleosomes stack on top of each other with parallel alignment of their dyad axes (δ). P corresponds to the distance between the DNA gyres measured at the front side of the particle. S corresponds to the stacking repeat. (F) In the columnar isotropic phase observed by thin film cryoEM, columns of nucleosomes form a random network sketched in (E). Nucleosomes are recognized in side (arrows) and top (arrowheads) views. (B and F) White arrows indicate the orientation of the nucleosome's dyad axis δ where it lies in the observation plane. Black arrows point to side view particles with their dyad axis out of the observation plane. (G) Distribution of P-values measured in the lamello-columnar and columnar isotropic phases.