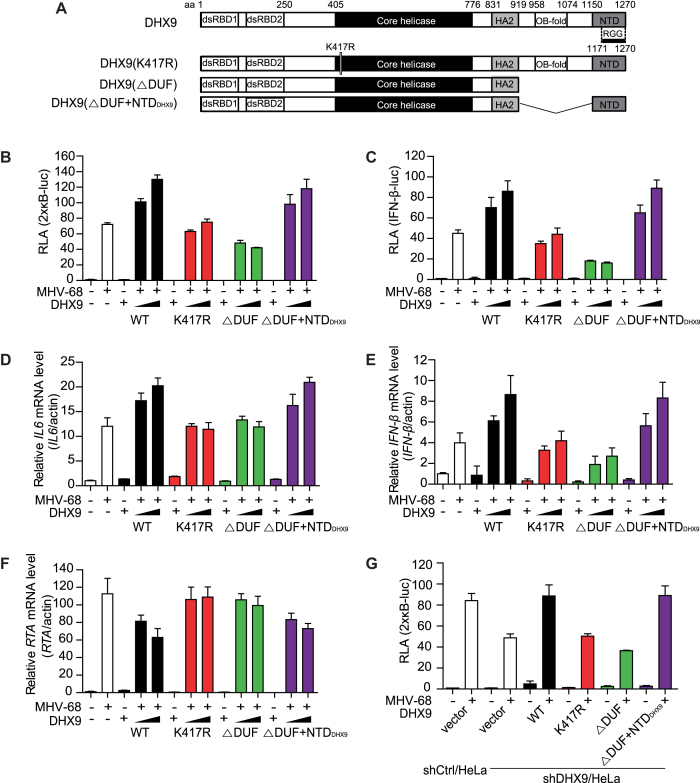
Figure 4.
The ATPase/helicase activity, not the cytosolic DNA-sensing domain of DHX9 is required for induction of IL6 and type I IFN upon MHV-68 infection. (A) Schematic diagrams of DHX9 domains and its deletion mutants. The numbers represent the positions of DHX9 amino acid residues that delineate the domains. dsRBDs, double-stranded RNA-binding domains; HA2, helicase-associated domain 2; OB-fold, oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding; NTD, nuclear transport domain; and RGG-box, glycine-rich domain. K417R represents a substitution mutant of DHX9 Lys 417 to Arg that abrogates the ATP-dependent helicase activity, while DUF is a domain responsible for cytosolic DNA sensing. (B, C) HeLa cells in 24-well plates were transfected with 2 × кB-luc (B) or IFN-β-luc (C) reporter plasmid (100 ng) and various DHX9 mutants (200 or 400 ng) for 20 h, followed by infection with MHV-68 at MOI 2 for another 12 h, and harvested for a luciferase assay. (D–F) HeLa cells in 12-well plates were transfected with various DHX9 mutants (1 or 2 μg) for 24 h, and either mock-infected or infected with MHV-68 at MOI 2 for 12 h, total RNAs were extracted for RT-qPCR. The relative levels of IL6 (D), IFN-β (E) and MHV-68 RTA (F) mRNAs were determined using ACTIN as a control. (G) shCtrl/HeLa and shDHX9/HeLa cells were transfected with 2 × кB-luc (100 ng) and various DHX9 mutants (200 or 400 ng) for 20 h, followed by infection with MHV-68 at MOI 2 for another 12 h, and the cells were harvested for a luciferase assay. The data represent mean ± SD of triplicate assays.