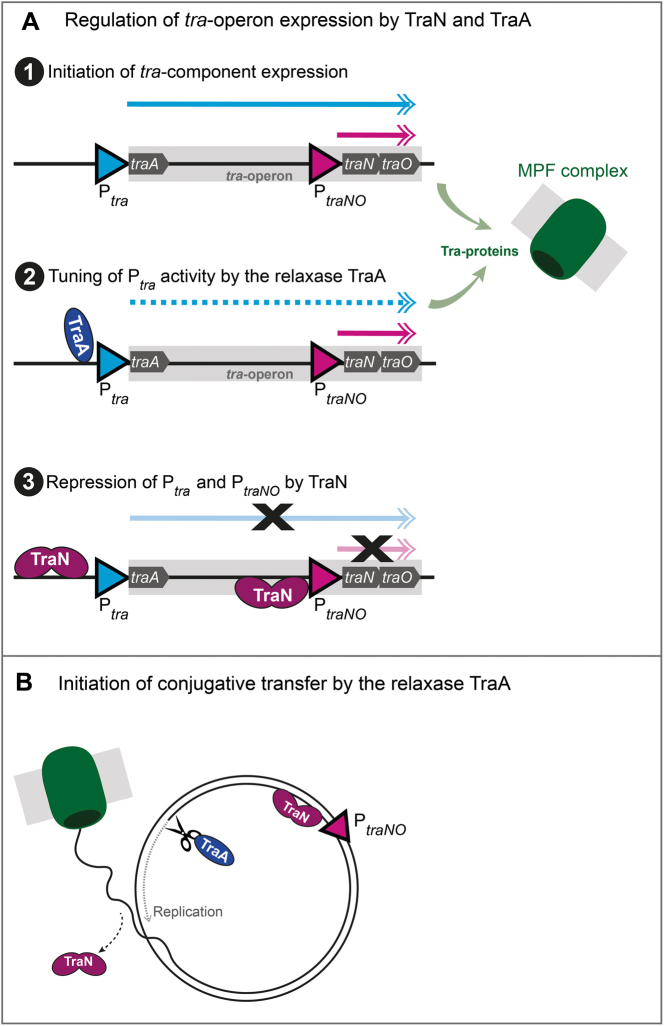
Figure 8.
Scheme of the proposed regulation of pIP501 by TraN and the relaxase TraA. (A) Regulation of tra-operon expression by TraN and TraA. (1) The expression of Tra-proteins from the tra-operon is initiated and mRNA is produced from the Ptra and the PtraNO promoters. (2) The relaxase TraA binds to its binding site at the Ptra promoter and controls the level of tra-operon transcription, while the PtraNO promoter remains active. Simultaneously, Tra-proteins are produced and the mating pair formation (MPF) complex assembles at the bacterial membrane. (3) TraN binding to its binding sites upstream of the Ptra and the PtraNO promoters leads to repression of transcription. (B) Initiation of conjugative transfer by the relaxase TraA. Responding to yet unknown signals, conjugative processes are initiated by the relaxase TraA introducing a single-strand (ss) cut at the origin of transfer (oriT). TraN is released from its binding site at the Ptrapromoter and replication takes place in the donor, while the ss-DNA is transferred to the recipient.