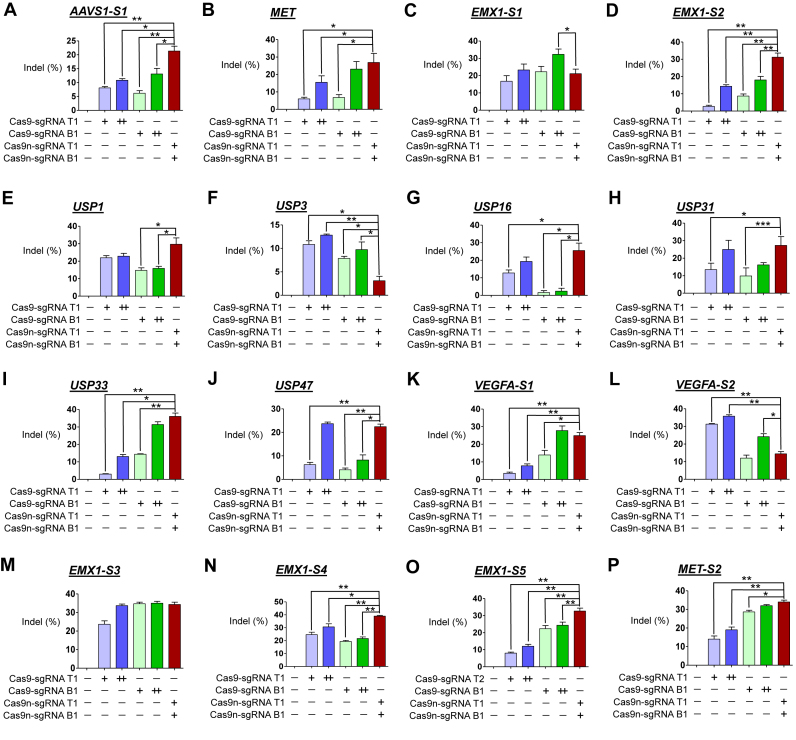
Figure 2.
Gene disruption efficiencies of paired Cas9 nickases vs. double the amount of Cas9 nucleases using sgRNA (5′GX20 or 5′GX19) without control sgRNA in human cells. (A–P) Cas9 paired nickase- or nuclease-driven mutations in the human genes detected by the T7E1 assay. HEK293T were analyzed 3 days after transfection with plasmids encoding paired Cas9 nickases or Cas9 nuclease, 5′GX20 sgRNAs targeting AAVS1-S1 (T1 and B1; A), MET (T1 and B1; B), EMX1-S1 (T1 and B1; C), EMX1-S2 (T1 and B1; D), USP1 (T1 and B1; E), USP3 (T1 and B1; F), USP16 (T1 and B1; G), USP31 (T1 and B1; H), USP33 (T1 and B1; I), USP47 (T1 and B1; J), VEGFA-S1 (T1 and B1; K), and VEGFA-S2 (T1 and B1; L). HEK293T were analyzed 3 days after transfection with plasmids encoding paired Cas9 nickases or Cas9 nuclease, 5′GX19 sgRNAs targeting EMX1-S3 (T1 and B1; M), EMX1-S4 (T1 and B1; N), EMX1-S5 (T2 and B1; O) and MET-S2 (T1 and B1; P). The frequency of Cas9 nuclease- or paired nickases-driven mutations as determined by the T7E1 assay are shown using bar graph. Error bars were derived from three independent experiments (n = 3). For brevity, statistical significance was shown only for comparison between a group-of-interest and the paired nickase group, except for the negative control group; *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001 by paired t-test. ‘+’ and ‘++’ denote 1 and 2 μg concentrations of Cas9 nucleases or paired Cas9 nickases using top or bottom sgRNAs, respectively.