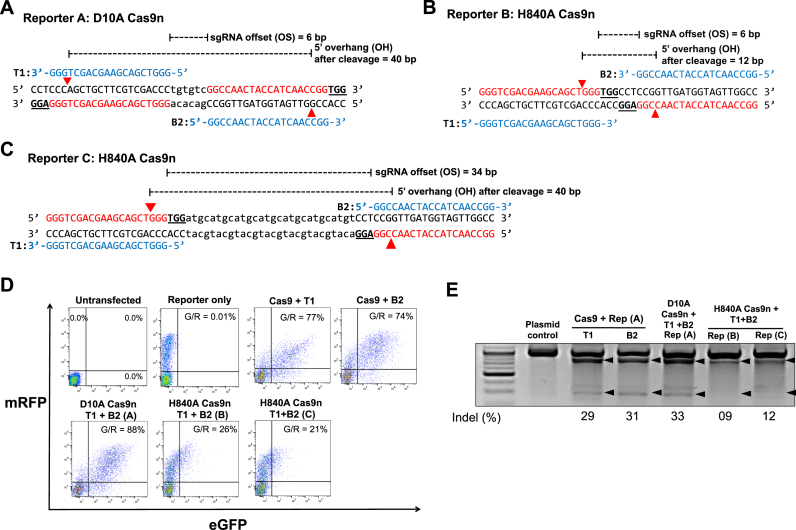
Figure 6.
Comparison of indel generation efficiencies of paired Cas9 D10A nickases vs. paired Cas9 H840A nickases using identical 5′GX20 sgRNAs without control sgRNA. (A–C) Three surrogate reporters containing sequences that can be targeted with a fixed sgRNA pair (T1 and B2; shown in blue letters) were constructed. sgRNA target sites (T1 and B2) are indicated by red letters and PAM sequences are marked by bold underlined letters. (A) A sequence that can be targeted by D10A Cas9n and the sgRNA pair with a +6 bp offset. The cleavage is expected to lead to a 40 bp 5′ overhang. (B) A sequence that can be targeted by H840A Cas9n and the sgRNA pair with a +6 bp offset. The cleavage is expected to lead to a 12 bp 5′ overhang. (C) A sequence that can be targeted by H840A Cas9n and the sgRNA pair with a +28 bp offset. The cleavage is expected to lead to a 40 bp 5′ overhang. (D–E) HEK293T cells were analyzed 3 days after transfection with a plasmid encoding Cas9 nickase (D10A or H840A) or double the amount of Cas9 nuclease, plasmids encoding sgRNAs (T1 and B2), and a reporter plasmid containing the target sequence shown above (A, B or C). (D) Representative flow cytometry. The percentages of GFP+ cells in the total RFP+ cell population (G/R) are shown (e.g. G/R = 77%). (E) The mutation frequencies in the target sequence of the transfected reporter plasmids detected by the T7E1 assay.