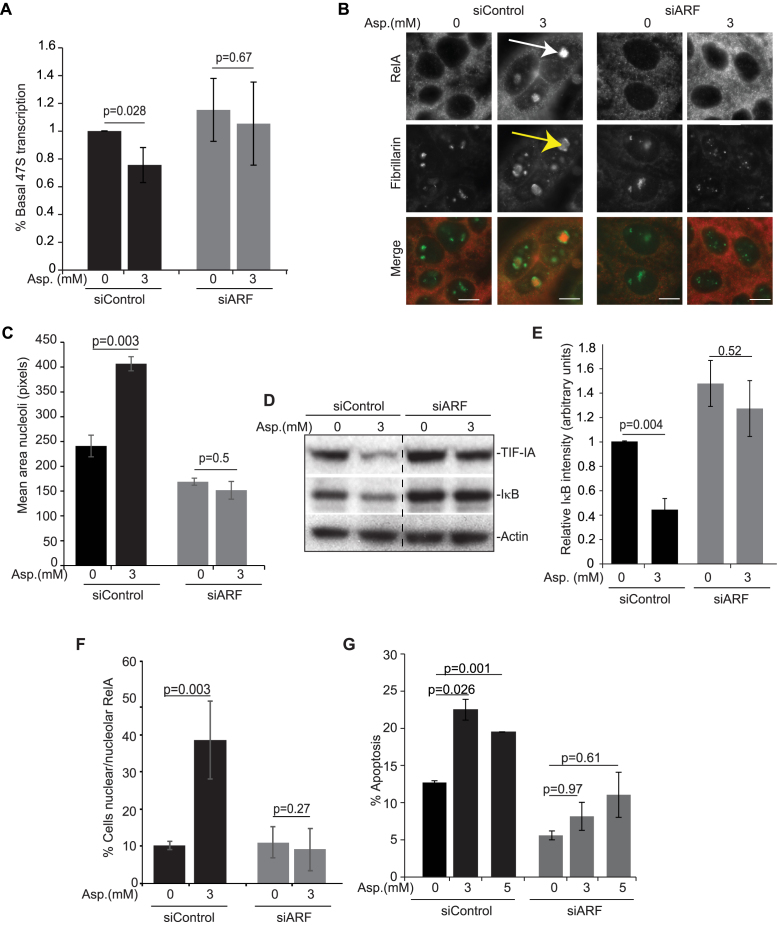
Figure 6.
Blocking TIF-IA degradation inhibits aspirin effects on nucleoli and the NF-κB pathway. (A–G) Blocking TIF-IA degradation, using siRNA to p14ARF, abrogates aspirin-mediated inhibition of rDNA transcription, nucleolar enlargement, degradation of IκB, nuclear/nucleolar translocation of RelA and apoptosis. SW480 cells were transfected with control or p14ARF siRNA as in Figure 6 then treated with aspirin (Asp.) at the concentrations specified. (A) qRT-PCR with primers for the 47S pre-rRNA transcript measured levels of rRNA transcription. GAPDH was used to normalise. Results are presented as the percentage of relative 47S transcription compared to the equivalent 0mM control for each siRNA. Mean (±s.e.m.) of 3 is shown. (B) Immunocytochemistry was performed on fixed cells with the indicated antibodies. Arrows indicate nucleolar RelA (white) and enlarged, segregated nucleoli (yellow). (C) Nucleolar area was quantified in at least 150 cells using IPlab software with fibrillarin as a nucleolar marker. Mean (± s.e.m.) is shown. N = 3. (D) Immunoblots demonstrating cytoplasmic levels of IκBα. (E) ImageJ software measured IκBα intensity relative to actin. The results are the mean of 3 experiments ±s.e.m. (F) Immunocytochemistry was performed as in B. The percentage of cells in the population showing nucleolar RelA was quantified manually. At least 6 fields of view and >100 cells were analysed per condition. The mean ± s.e.m is shown. N = 3. (G) Annexin V apoptosis assays were performed. The percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis was determined by fluorescent microscopy. At least 200 cells were analysed for each sample. The results are the means of two independent experiments ± s.e.m. Actin acts as a loading control. Scale bar = 10 μm. P values were derived using a two-tailed Student's t test. N values are biological repeats.