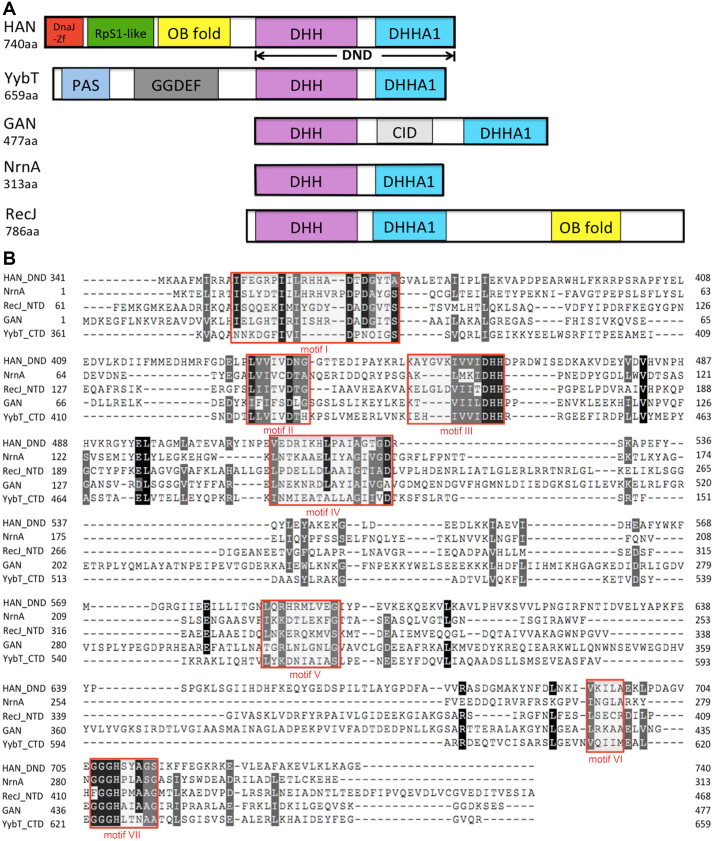
Figure 1.
Schematic representation and multi-alignment of HAN-related DHH phosphoesterase superfamily members. (A) Schematic representation of HAN, NrnA, GAN (also called archaeal RecJ), YybT and RecJ. DHH and DHHA1 indicate that the DHH domain consists of motifs I-V, and the DHHA domain consists of motifs VI and VII (motif VII is classified into DHHA1 or DHHA2 motif, based on the sequence conservation). DnaJ-Zf, RpS1-like, OB-fold, CID, PAS and GGDEF denote DnaJ type Zn-finger, ribosomal protein S1-like, and oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold, CMG interaction domain, and Per-Arnt-Sim that are required for heme-binding and GGDEF, which originates from the conserved amino acid motif GGDEF in diguanylate cyclase, domains, respectively. (B) Sequence multi-alignment of PfuHAN and other family members of the DHHA1 phosphodiesterase subsuperfamily. One typical protein was selected from the HAN, Nrn, GAN, YybT and RecJ families and used for multi-alignment with the ClustalW programme. These proteins are PfuHAN (AAL80523), T. kodakarensis GAN (TkoGAN, BAD85441), Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) NrnA (BsuNrnA, NP_390803), B. subtilis RecJ (NP_390640), and B. subtilis YybT (NP_391931.1). For clarity, only DHH and DHHA1 domains from PfuHAN (PfuHAN_DND, aa341–740), N-terminal domain of BsuRecJ (BsuRecJ_NTD, aa61–468, i.e., the catalytic core of bacterial RecJ), and C-terminal domain of BsuYybT (BsuYybT_CTD, aa361–659) are used for multi-sequence alignment. Completely and partially conserved residues between the sequences are shaded in dark and light, respectively. Motifs I-VII are marked with red rectangles.