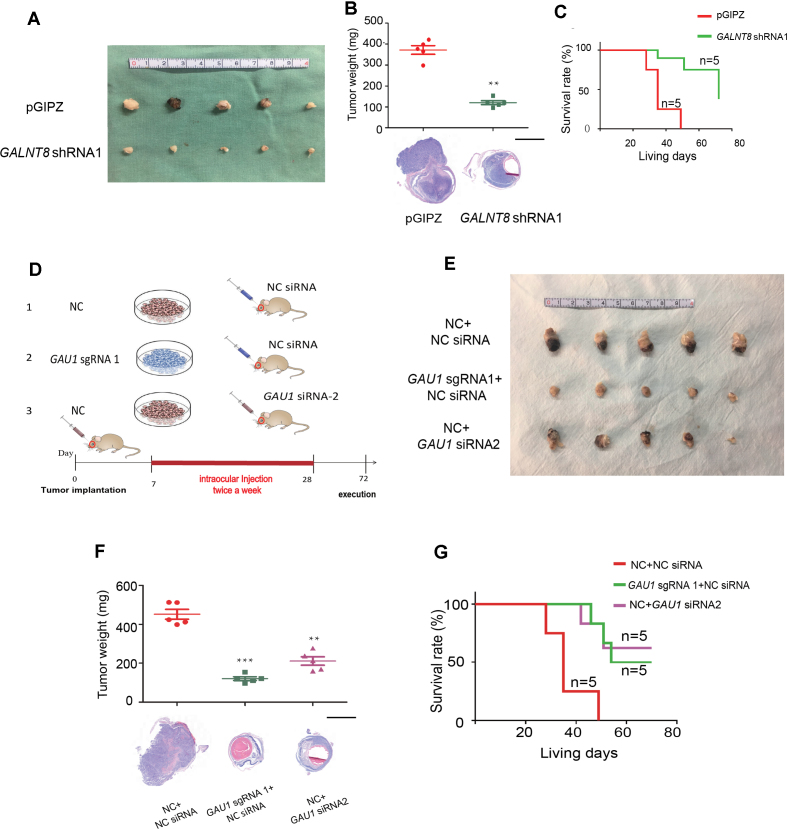
Figure 3.
Suppression of the GAU1/GALNT8 cluster elicits a therapeutic effect in vivo. (A) Schematic of the animal experiment group. Group A: control cells were injected into the vitreous, and scrambled siRNA was subsequently injected into the vitreous with an HKP vector twice per week (from the 7th day to 28th day after implantation); Group B: GAU1 knockdown cells were injected and scrambled siRNA was administered as described above; and Group C: negative control cells were injected and GAU1 siRNA was administered as described above. (B): Representative image of the orthotopic xenograft formed by Y79 cells injected into the vitreous with or without GAU1 knockdown by sgRNA or siRNA at 40 days after implantation; n = 5. (C) Top: bar graph shows tumor volumes formed by the indicated Y79 cells in mouse vitreous. Bottom: representative images of H&E staining for the evaluation of tumor formation. n = 5; scale bar: 2 mm. (D) Survival analysis of mice following vitreous implantation with Y79 cells with or without GAU1 knockdown by sgRNA or siRNA; n = 5. (E) General photograph of orthotopic xenograft at 40 days after implantation by the injection of Y79 cells into the vitreous with or without GALNT8 knockdown; n = 5. (F) Top: bar graph shows tumor volumes formed by the indicated Y79 cells in mouse vitreous. Bottom: representative images of H&E staining for the evaluation of tumor formation. n = 5; scale bar: 2 mm. (G) Survival analysis of mice following vitreous implantation with Y79 cells with or without GALNT8 knockdown; n = 5.