Figure 2. Provitamin A carotenoid metabolism in the intestine of of Isx-/-mice.
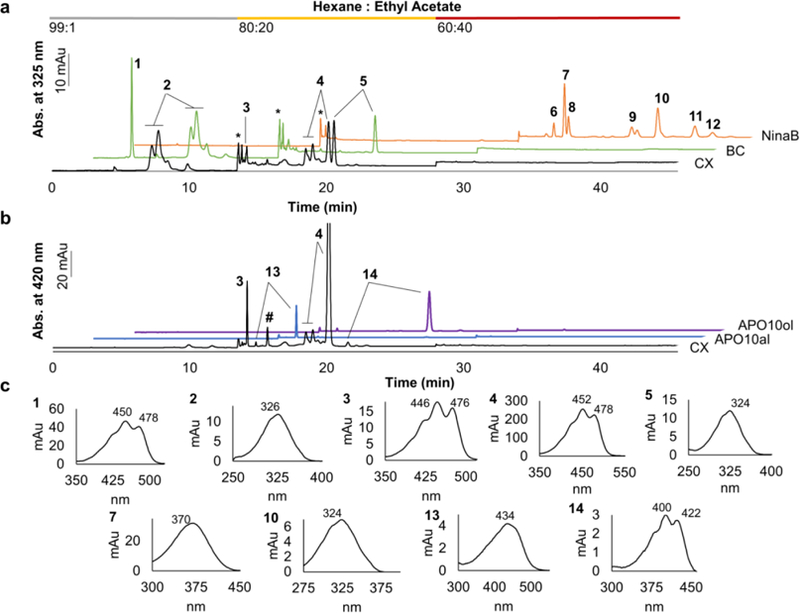
Shown are HPLC traces of intestinal lipid extracts from mice. a. A three step gradient HPLC system was applied to separate nonpolar (0 to 12 min), slightly polar (12 to 28 min) and polar (28 to 44 min) carotenoids and apocarotenoids by mixing hexane with ethyl acetate at different ratios (indicated at the top of the diagram). The diagram displays the HPLC trace at 325 nm of lipid extracts of Isx-/-mice supplemented with CX (black trace) or BC (green trace). The orange trace represents a lipid extract of an enzyme assay of insect NinaB incubated with ZEA. Peaks were identified by retention time and spectral characteristics. b. The diagram displays the HPLC trace at 420 nm of a lipid extract of Isx-/-mice supplemented with CX (black trace). The blue trace represents the APO10al and the purple trace the APO10ol standard. c. Spectral characteristics of peaks identified in a and b are shown. The individual peaks represent 1, BC; 2, retinyl ester; 3, 3-oxo-CX; 4, CX (includes both all-trans and cis isomers); 5, all-trans-retinol; 6, 3-hydroxy-13-cis-retinal; 7, all-trans-3-hydroxy-retinal; 8, 11-cis-3-hydroxy-retinal; 9, ZEA; 10, all-3-hydroxy-trans-retinol; 11, 11-cis-3-hydroxy-retinol; 12, ZEA isomer; 13, APO10al; 14, APO10ol; *, solvent peak; #, unidentified peak.
