Fig. 1.
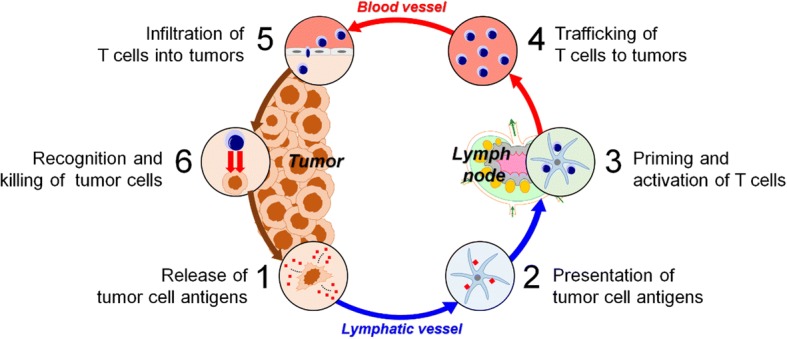
Cancer–immunity cycle. Tumor antigens released from tumor cells are recognized by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Matured APCs migrate to the lymph nodes, leading to priming and proliferation of T cells. T cells activated by APCs are transferred to tumor tissues, where they kill tumor cells. Finally, tumor antigens from killed cancer cells induce another round of the immune response, leading to a cancer–immunity cycle
