Figure 3.
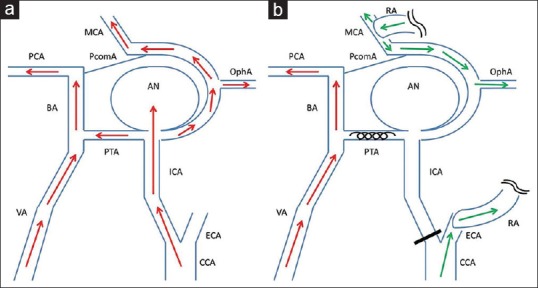
Schematic drawing of the surgery. Preoperative (a) and postoperative (b) hemodynamics are shown. The aneurysm was located at internal carotid artery-primitive trigeminal artery bifurcation, and received anterograde flow from internal carotid artery. Coil embolization of primitive trigeminal artery and ligation of internal carotid artery at cervical portion followed by construction of the external carotid artery-radial artery-M2 bypass prevented anterograde blood flow into the aneurysm from both internal carotid artery and primitive trigeminal artery. Intradural internal carotid artery territory including ophthalmic artery (OphA) was perfused by bypass flow. Red arrows: anterograde blood flow from internal carotid artery and vertebral artery, green arrows: Blood flow from external carotid artery-radial artery-M2 bypass, AN aneurysm, BA: Basilar artery, CCA: Common carotid artery, MCA: Middle cerebral artery, PCA: Posterior cerebral artery, PcomA: Posterior communicating artery
