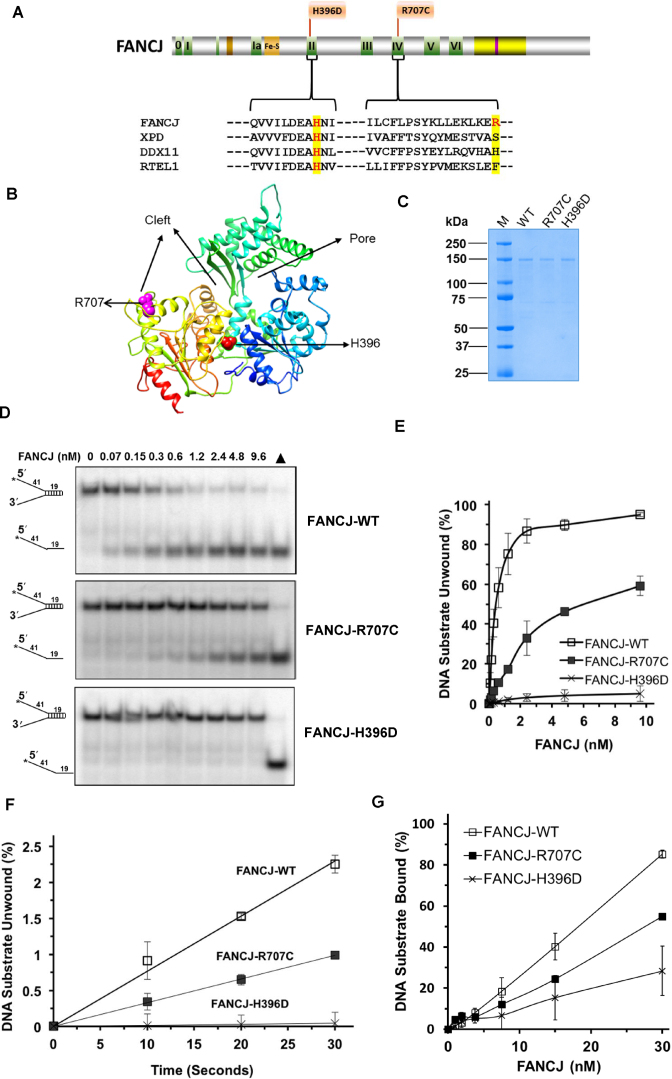
Figure 1.
FA-linked FANCJ-R707C and FANCJ-H396D mutations and their biochemical characterization. (A) Human FANCJ depicting helicase core domain with canonical motifs indicated by colored boxes and FA-linked FANCJ mutations R707C and H396D are shown. The conservation in motif II and IV is shown with the sequence alignment of human FANCJ, XPD, DDX11 and RTEL1. BLM binding region (yellow) and BRCA1 binding site (purple) are shown. (B) Predicted structure of FANCJ based on TaXPD (28) as a template using Phyre2 (61). The locations of R707 and H396 are shown in pink and red, respectively. Based on TaXPD structure, the cleft and pore in the modeled structure of FANCJ is highlighted. (C) A Coomassie-blue stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel showing 2 μg of purified homogenous recombinant proteins FANCJ-WT, FANCJ-R707C, and FANCJ-H396D. kD (kilodalton) represents molecular mass protein standards. (D) FANCJ mutations H396D and R707C differentially affected DNA helicase activity. Representative native polyacrylamide gel images showing helicase reaction products from reaction mixtures containing the indicated FANCJ proteins incubated with 0.5 nM forked duplex (19 bp) DNA substrate at 30°C for 15 min as described in Materials and Methods. Filled triangle represents heat-denatured DNA substrate control. (E) Quantitative analysis of helicase activity by FANCJ proteins is shown with standard deviation (S.D.) indicated by error bars. Open square, FANCJ-WT; filled square, FANCJ-R707C; open cross, FANCJ-H396D. (F) Unwinding kinetics by FANCJ helicase proteins as determined by protein trap kinetics assays. Reactions with the indicated FANCJ protein (FANCJ-WT (0.6 nM), FANCJ-R707C (1.9 nM), or FANCJ-H396D (4.8 nM)) in the presence of 5 nM forked duplex (19 bp) DNA substrate were initiated by simultaneous addition of 100-fold excess of dT200 oligo (serve as protein trap) and ATP at 30°C and aliquots quenched at 5 s intervals. Quantitative analyses of DNA unwinding by FANCJ-WT (open square), FANCJ-R707C (filled square), and FANCJ-H396D (open cross) under conditions simulating single-turnover are shown. (G) DNA binding by FANCJ wild-type and mutant proteins. The indicted concentrations of the specified FANCJ protein were incubated with the forked duplex (19 bp) DNA substrate (0.5 nM) at 24°C for 30 min. Radiolabeled DNA and protein-DNA complexes were resolved by EMSA (Supplementary Figure S1), as described in Materials and Methods. Quantitative analysis of % DNA substrate bound by FANCJ is shown with S.D. indicated by error bars. Open square, FANCJ-WT; filled square, FANCJ-R707C; open cross, FANCJ-H396D.