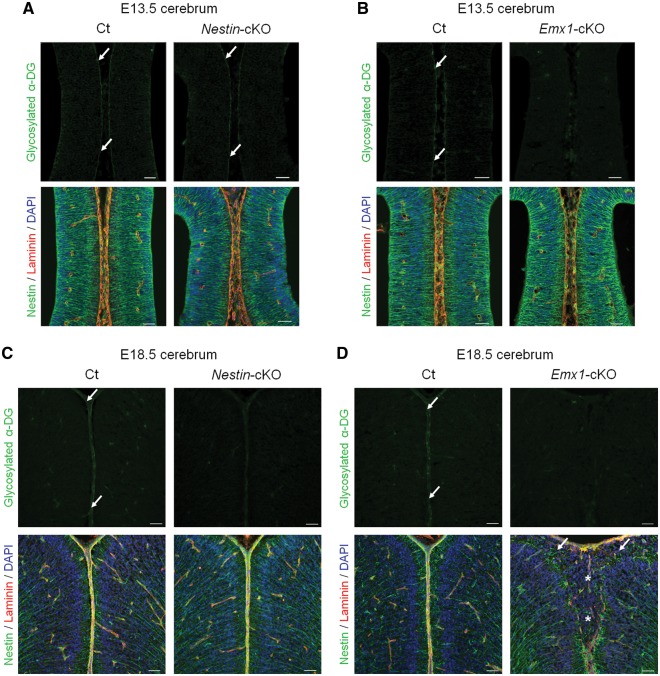
Figure 3.
Dystroglycan glycosylation and phenotypic correlation during brain development in fukutin-cKO mice. (A, B) Immunofluorescence analysis of the developing cortex at E13.5. (A, upper panel) Nestin-fukutin-cKO mice demonstrated residual glycosylation of α-DG at the glia limitans as in littermate controls (arrow). (B, upper panel) Defective glycosylation of α-DG was observed in Emx1-fukutin-cKO mice. (A and B, lower panel) Both strains exhibited almost normal brain structure regardless of α-DG glycosylation state. (C, D) Immunofluorescence analysis of the developing cortex at E18.5. (C and D, upper panel) Both strains demonstrated defective glycosylation of α-DG in contrast to littermate controls. (C, lower panel) With the exception of focal cortical dysplasia within a limited region, the laminar organization of the cerebral cortex and basement membrane were preserved in Nestin-fukutin-cKO mice. (D, lower panel) Diffuse and severe brain malformations were observed in Emx1-fukutin-cKO mice, in contrast to very mild brain pathology in Nestin-fukutin-cKO mice. Cerebral hemispheres were widely fused (asterisk), and the glia limitans-basement membrane complex was diffusely dissociated in Emx1-fukutin-cKO mice. Many ectopic cells were observed in the subarachnoid space (arrow). Scale bars = (A, B, C, D) 50 μm.