Figure 1.
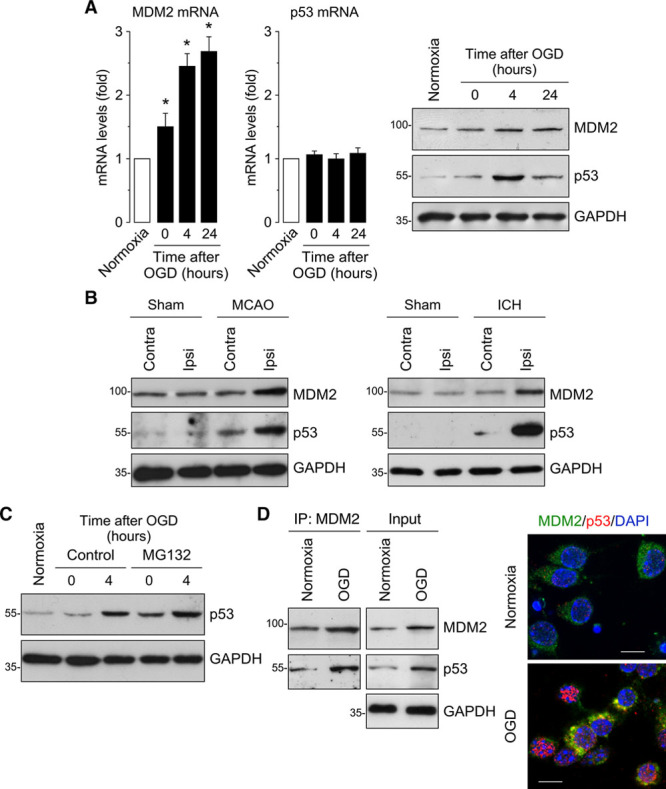
Ischemia upregulates MDM2 expression, which interacts with p53. A, Time course of MDM2 (murine double minute 2) and p53 mRNA levels measured by RT-qPCR (quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) showing increased MDM2 mRNA levels in primary neurons after oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD), whereas p53 mRNA remained unchanged. Representative Western blot images showing MDM2 and p53 protein levels in neurons after OGD. Quantification of protein levels is shown in Figure I in the online-only Data Supplement (n=4 neuronal cultures). B, Mice were subjected to ischemic (transient middle cerebral artery occlusion [tMCAO]) or intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH; collagenase injection) stroke models. Representative Western blot images showing MDM2 and p53 protein levels in the contralateral (contra) and ipsilateral (ipsi) hemispheres at 24 h after tMCAO, ICH, or Sham surgery (n=4 mice). Quantification of protein levels is shown in Figure II in the online-only Data Supplement (n=4 mice). C, Neuronal treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10 µmol/L) promoted a time-dependent accumulation of p53. Quantification of protein levels is shown in Figure I in the online-only Data Supplement (n=4 neuronal cultures). D, MDM2 and p53 proteins interact at 4 h after OGD, as shown by both coimmunoprecipitation assay and immunocytochemistry (GAPDH as loading control). Representative images are shown (green, MDM2; red, p53; blue, DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole); scale bar=10 µmol/L). Data are expressed as mean±SEM from 4 different neuronal cultures. MCAO indicates middle cerebral artery occlusion. *P<0.05 compared with normoxia.
