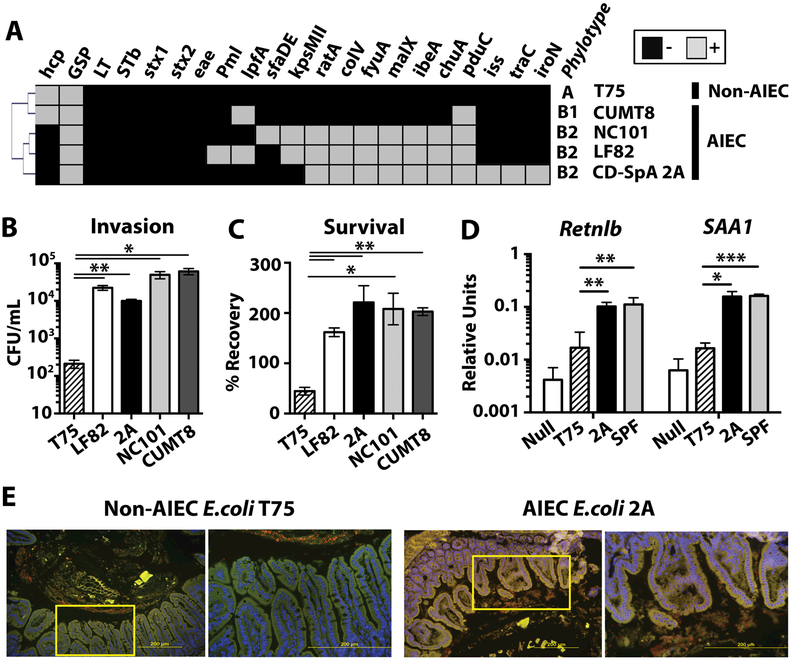
Fig 3. CD-SpA-derived Adherent-invasive E. coli (AIEC) initiates epithelial immunity.
A. The presence (gray) or absence (black) of AIEC-associated virulence factors genes was determined by PCR for E. coli isolates T75 (non-AIEC), CUMT8 and NC101 (mouse-derived AIEC), LF82 (human-derived AIEC), and CD-SpA isolate 2A. Hierarchical clustering was performed using average linkage clustering and Pearson correlation distance metric. B. Invasion of Caco-2 cells by E. coli isolates was assessed by gentamicin protection assay. The mean colony forming units (cfu) / ml is presented. C. Survival in J774 macrophages by E. coli isolates was assessed by gentamicin protection assay. The percentage of input cfu recovered following gentamicin protection in J774 macrophages is shown. SEM is shown for each group. p-values *<0.05, **<0.01 are indicated, T-test. All samples were run in triplicate with N=3–5 biological replicates for each group. D. qPCR analysis of Retnlb and SAA1 expression by ileal epithelial cells 5 days after colonization with SPF microbiota, CD-SpA E. coli 2A, non-AIEC T75 or media control. Bar graph represent the geometric mean for 4–8 mice / group from 2 independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. p-values *<0.05, **<0.01 are indicated, ANOVA. E. FISH of ileal mucosa 5 days after mono-colonization with E. coli isolate T75 or 2A. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) and an E.coli are stained with a 16S rRNA probe (red). Tissue autofluorescence is in green. Yellow box indicates inset displayed in the right panel.