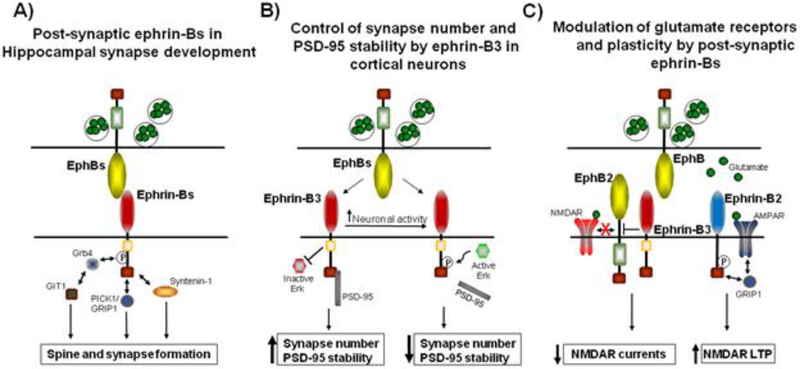
Figure 3.
Post-synaptic ephrin-Bs regulate synapse development and function. (A) Ephrin-Bs regulate post-synaptic development by interacting the Syntenin-1, interacting with the AMPAR-binding proteins PICK1 and GRIP1, and by interacting with Grb4, which recruits GIT1 to synapses. (B) In cortical neurons, ephrin-B3 controls synapse number by inhibiting Erk1/2 and by interacting with the MAGUK scaffolding protein PSD-95. Upon increased neuronal activity, Erk1/2 becomes activated and phosphorylates ephrin-B3 at S332. Phosphorylation of ephrin-B3 disrupts the interaction with PSD-95 and disperses PSD-95 from synapses. (C) Ephrin-Bs regulate glutamate receptor signaling at synapses. Ephrin-B2 interacts with AMPARs through GRIP1, which promotes the surface retention of AMPARs and promotes NMDAR-dependent LTP. Ephrin-B3 interacts in cis with EphB2, which attenuates EphB2 activation. Decreased EphB2 activity results in a decrease in phosphorylation of GluN2B at Y1472 which in turn decreases NMDAR currents.