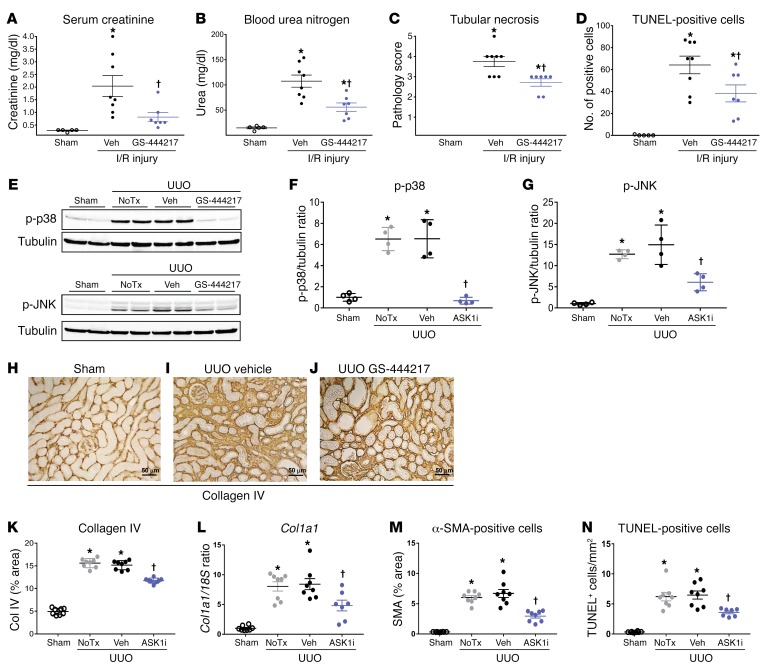
Figure 5. GS-444217 inhibits acute renal tubular injury in rat kidney.
(A–D) Renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. GS-444217 (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (Veh; equal volume) was orally administered to Sprague-Dawley rats just before 30 minutes of bilateral renal ischemia. Parameters of renal function were assessed in serum and kidney following a 24-hour reperfusion period. (A and B) Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen concentrations. (C and D) Renal pathology scores for tubular necrosis (H&E-stained sections) and apoptosis/necrosis (TUNEL stain). Data in A–D are mean ± SEM, n = 5–8; *P < 0.05 vs. control, †P < 0.05 vs. I/R treated with vehicle (ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons test). (E–N) Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Sprague-Dawley rats had sham or UUO surgery. GS-444217 (30 mg/kg) or vehicle (equal volume) was orally administered 1 hour before surgery and continued twice per day for 7 days. (E–G) Western blot analysis of kidney lysates for p-p38 and p-JNK. Dot plots show p-p38 and p-JNK levels normalized to tubulin loading control (NoTx, no treatment). (H–K, M, and N) Image analysis and graphed pathology scores of renal sections stained for collagen deposition (collagen IV) (scale bars: 50 μm) (H–K), cortical interstitial α-smooth muscle actin–positive (α-SMA–positive) myofibroblasts (M), and apoptosis/necrosis of kidney epithelial cells (TUNEL) (N). (L) Collagen I (Col1a1) mRNA was measured in whole kidney by reverse transcriptase PCR. Data in F, G, and K–N are mean ± SEM, n = 4 (sham), n = 8 (UUO); *P < 0.01 vs. sham surgery, †P < 0.01 vs. UUO treated with vehicle (ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons test).