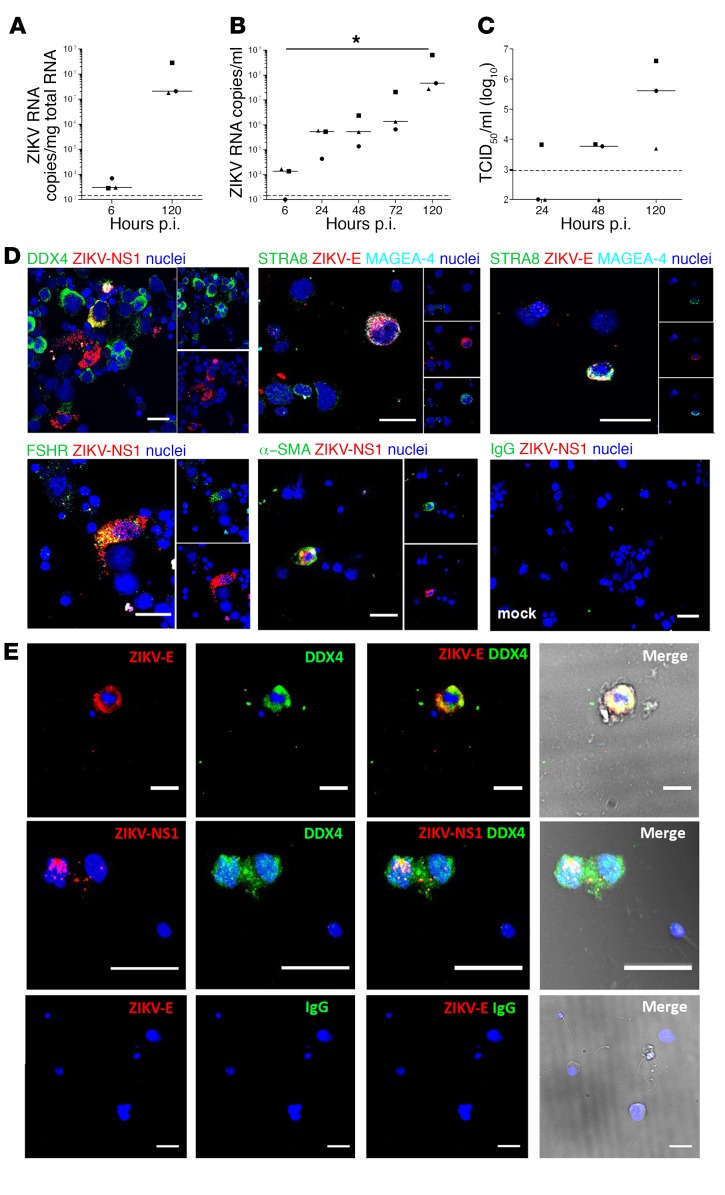
Figure 4. ZIKV replicates in human testicular germ cells in vitro and in vivo.
(A–C) Primary testicular cells were infected with ZIKV (MOI of 1, corresponding to 7.15 × 105 TCID50 U/ml per 0.5 million cells). ZIKV RNA detected by RT-qPCR in cells (A) and culture supernatants (B). (C) Viral titers determined by infectivity assay of tissue supernatants on VeroE6 cells. Each dot represents an independent donor. Bars represent median values. Dotted lines indicate detection limit. *P < 0.05 (Friedman-Dunn nonparametric comparison). (D) Immunofluorescence against ZIKV NS1 or ZIKV-E proteins combined with cell markers for all germ cells (DDX4) or specific germ cell types (STRA8, MAGEA-4), Sertoli cells (FSHR), and peritubular cells (α-SMA). Nuclei are stained in blue. (E) Detection of infected germ cells in semen from ZIKV-infected men. Immunofluorescence labeling of semen cell smears from 2 ZIKV-infected patients, one on day 7 (top row) and one on day 11 (middle row) after onset of symptoms. ZIKV-E or NS1 protein colabeled with the germ cell marker DDX4. Bottom panels show semen from a healthy individual stained with anti–ZIKV-E antibody and IgG isotype as a negative control. Nuclei are stained in blue. In the merge panels, brightfield images are included to visualize the cell’s morphology. Scale bars: 20μm.