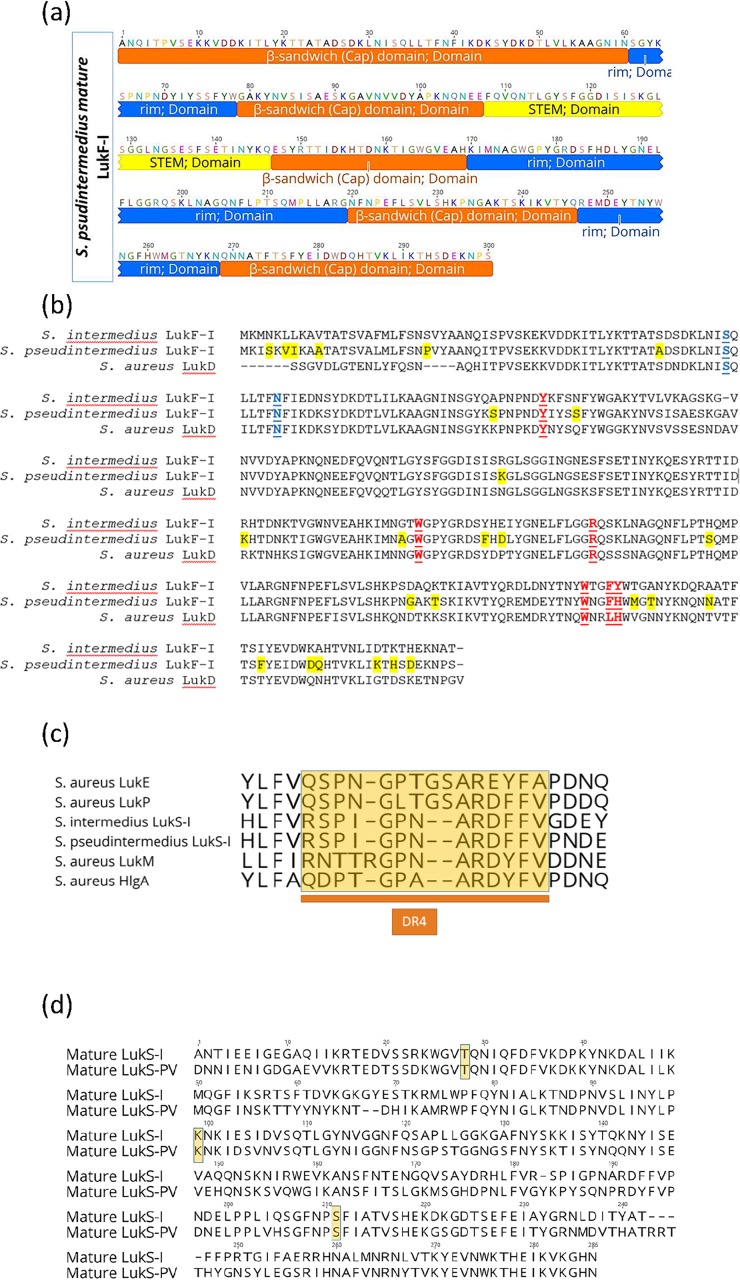
Fig 3. Unique residues in S and F-components of S. pseudintermedius Luk-I may shape the protein function and specificity.
A, domain structure of S. pseudintermedius LukF-I consist of β-sandwich (cap) domain highlighted in orange color (1–60, 79–107, 147–169, 220–246 and 569–300), stem highlighted in yellow (108–146) and rim highlighted in blue (61–78, 170–219 and 247–268). B, Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of S. intermedius and S. pseudintermedius LukF-I and S. aureus LukD. Geneious version 11.0.3 was used to generate the alignment. Residues unique to S. pseudintermedius LukF-I are highlighted yellow, residues identified as important for phospholipid interaction are shown in red and underlined text and residues important for oligomerization is highlighted in blue. C, MSA of amino acid sequences of the DR4 region (highlighted in yellow) in the rim domain (an important region for S-component receptor binding) of S. aureus LukE, HlgA, LukM and LukP, S. pseudintermedius LukS-I and S. intermedius LukS-I. The DR4 regions of S. aureus LukP and LukS-I of S. pseudintermedius and S.intermedius are almost identical, whilst that of LukM, HlgA and LukE are considerably different. D, MSA of amino acid sequences of S. pseudintermedius LukS-I and S. aureus LukS-PV showing the critical residues T28, K99 and S211 (highlighted in yellow) that interact with the corresponding F-component.