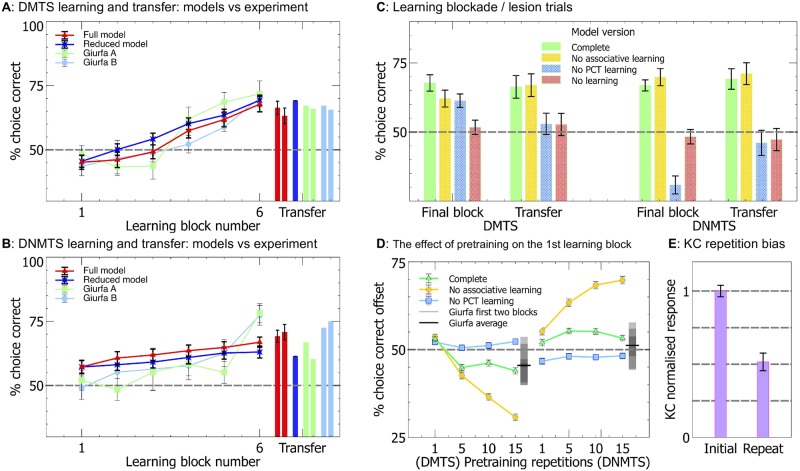
Fig 2. The full and reduced versions of our model reproduce the transfer of sameness and difference learning.
A & B The average percentage of correct choices made by the model and real bees within blocks of ten trials as the task is learned (lines), along with the transfer of learning onto novel stimulus sets (bars). Both versions of the model reproduce the pattern of learning acquisition for DMTS (Full: N = 338, Reduced: N = 360) and DNMTS (Full & Reduced: N = 360) found when testing real bees (test for learning: P <0.0001), along with the transfer of learning (P <0.0001). For DMTS Giurfa A & B are the data from Experiments 1 & 2 respectively from Giurfa et al. [8], and for DNMTS Giurfa A & B are the data from Experiments 5 & 6 respectively from the same source. For an explanation of the initial offsets from chance for the model please see the text for panel D. C The blockade of plasticity from the MB and PCT pathways shows that the PCT pathway is necessary and sufficient for sameness and difference learning in the full model. All non-overlapping SEM error bars are significantly different. D PCT pathway learning in the absence of associative learning leads to preference for non-matching stimuli following pre-training, demonstrating that learning in the associative pathway changes the form of the sameness and difference acquisition curves. The equivalent offsets and error ranges for the first two blocks of Giurfa Experiments 1, 2, 5 & 6 along with the averages for DMTS and DNMTS for these blocks are shown alongside the model data for comparison as overlapping grey boxes—overlapping boxes create darker regions, thus the area of greatest darkness is the point where the most of the error ranges overlap. E The average activity of the model KC neurons when presented with repeated stimuli.