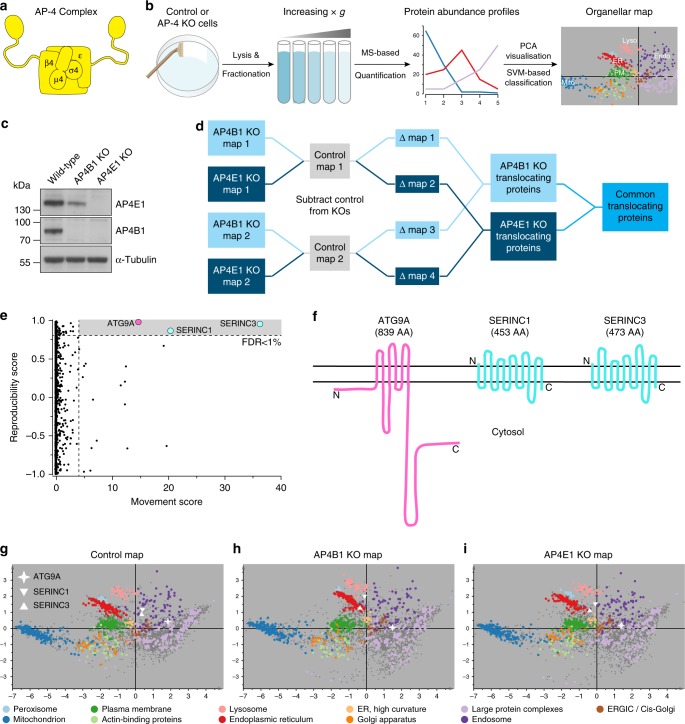
Fig. 1.
Dynamic Organellar Maps detect mislocalisation of ATG9A, SERINC1 and SERINC3 in AP-4 knockout (KO) HeLa cells. a Diagram of the AP-4 complex. b Workflow for Dynamic Organellar Map generation. Cell lysates are subjected to a series of differential centrifugation steps, to achieve partial separation of organelles. Proteins in each fraction are quantified by mass spectrometry (MS), to obtain abundance distribution profiles. Proteins associated with the same organelle have similar profiles. Clustering can be visualised by principal component analysis (PCA) and compartment assignments are made through support vector machine (SVM)-based classification. c Western blot of whole cell lysates from wild-type, AP4B1 KO and AP4E1 KO HeLa cells; α-Tubulin, loading control. Representative of two independent experiments. d Experimental design for AP-4 Dynamic Organellar Mapping. Maps were made from wild type, AP4B1 KO and AP4E1 KO cell lines, each in duplicate. Profiles from each KO map were subtracted from the cognate control profiles, to obtain two AP4E1 Δmaps, and two AP4B1 Δmaps. Proteins that did not shift had similar profiles in wild-type and AP-4 KO maps, and hence Δ profiles close to zero. To identify significantly translocating proteins, the magnitude of shift (M) and the reproducibility of shift direction (R) were scored for each protein and each Δmap. e MR plot analysis of AP-4 Dynamic Organellar Mapping. 3926 proteins were profiled across all maps. Three proteins whose subcellular localisation was significantly and reproducibly shifted across the AP-4 KO lines were identified with very high confidence (FDR < 1%). The analysis only covered proteins profiled across all maps; since AP-4 itself was not present in the KO maps, it was not included. See also Supplementary Data 1. f Topology of the proteins identified by AP-4 Dynamic Organellar Mapping. g–i Visualisation of organellar maps by PCA. Each scatter point represents a protein; proximity indicates similar fractionation profiles. Known organellar marker proteins are shown in colour, and form clusters. Each plot combines the data from two independent map replicates. g wild-type; h AP4B1 KO; i AP4E1 KO. The three proteins that undergo significant shifts in AP-4 KOs are annotated