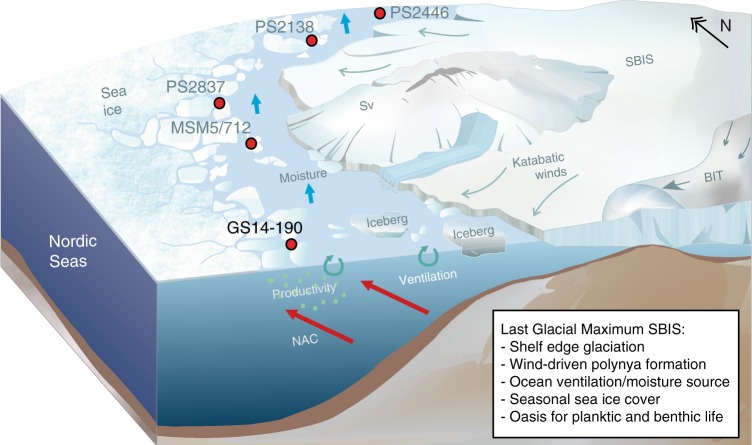
Fig. 7.
Schematic illustration of the polynyal activity in front of the western and northern Svalbard-Barents Sea ice sheet during the LGM as reconstructed from 5 sediment proxy records (Supplementary Table 1). Polynya activity is constrained by relatively high sea-ice diatom (IP25), marine organic phytoplankton and calcareous zooplankton production in all displayed sediment cores (this study)16,44,54,69,70 supported by sub-surface/intermediate inflow of Atlantic-water-derived waters (NAC) and katabatic winds. Coastal polynyas along the entire Svalbard-Barents Sea margin provided a constant source of moisture that sustained build-up of glacial ice, ventilation of deeper waters in the glacial Nordic Seas, and remained a refuge for marine and higher trophic terrestrial life in a polar desert. Sv: Svalbard, SBIS: Svalbard-Barents Sea Ice Sheet, BIT: Bear Island Trough, NAC: North Atlantic Current