Figure 2.
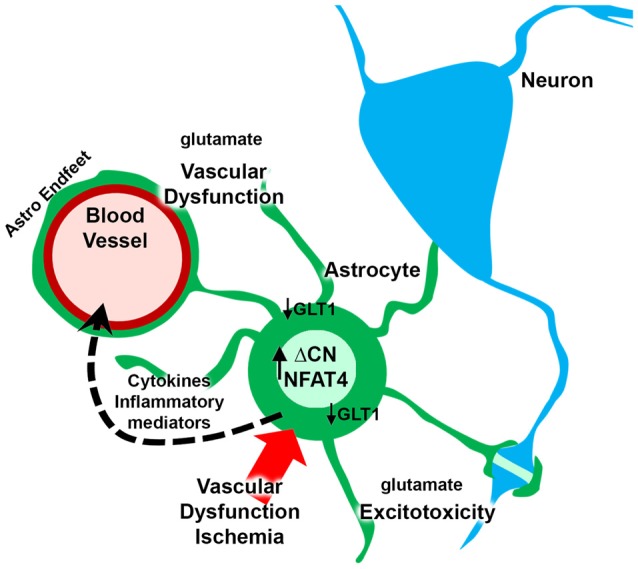
Putative role for astrocytic CN/nuclear factor of activated T cell (NFAT) in vascular dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Ischemia arising from vascular degeneration or disruption leads to increased expression of ΔCN and hyperactivation of NFAT4 in astrocytes. The CN/NFAT pathway induces numerous cytokines and other inflammatory mediators linked to neuroinflammation. Some of these factors may target blood vessels, leading to perivascular inflammation. CN/NFAT signaling also leads to the downregulation of GLT1 glutamate transporters resulting in elevated extracellular glutamate levels. Glutamate causes excitotoxicity at synaptic connections and disrupts astrocyte endfeet and/or blood brain barrier (BBB) integrity, leading to further vascular dysfunction and/or degeneration.
