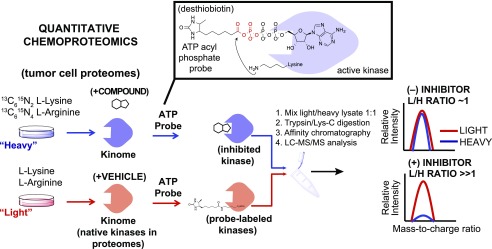
Fig. 4.
Quantitative chemoproteomics to define the target spectrum of ritanserin in tumor cell proteomes. Proteomes from lung tumor cells cultured in SILAC media are treated differentially with DMSO vehicle (light) or compound (heavy). Next, the ATP acyl phosphate probe is added to both light and heavy proteomes to label active kinase via covalent modification of conserved lysines in kinase active sites. Proteomes are digested to tryptic peptides using proteases. Active-site probe-labeled peptides are enriched by avidin affinity chromatography and quantified by LC-MS/MS. SILAC (light/heavy) ratios are used to evaluate compound activity at individual kinase active sites. No inhibition results in a SILAC ratio of approximately 1, whereas competition at respective kinase active sites blocks probe labeling and enrichment, resulting in SILAC ratios >>1 to identify targets of small molecule inhibitors. H, heavy; L, light.