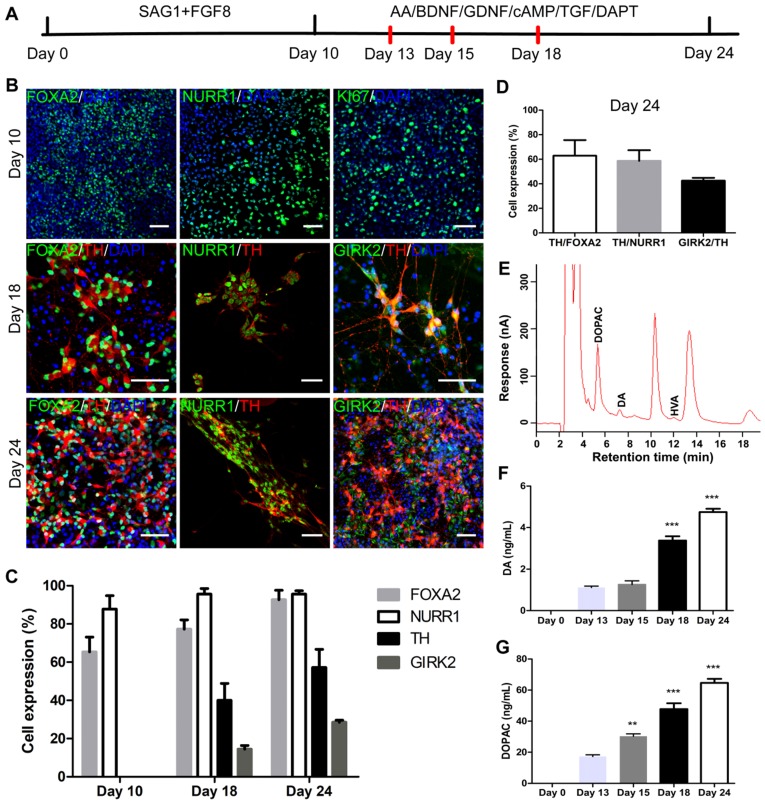
Figure 4.
iNSCs differentiate into midbrain dopamine neurons in vitro. (A) A schematic representation of the iNSC differentiation procedure in vitro. AA: ascorbic acid; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; GDNF: glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; TGF: transforming growth factor. (B) Immunofluorescent staining for FOXA2, NURR1, and KI67 on day 10, FOXA2, NURR1, GIRK2 and TH on days 18 and 24, on cells derived from P30 iNSC1. Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Efficiency of differentiation from P30 iNSC1 on days 10, 18 and 24 (n=3 independent experiments). (D) Percentages of TH/FOXA2, TH/NURR1, and GIRK2/TH on differentiation day 24. (E) DA, DOPAC and HVA levels secreted by iNSC-derived midbrain dopamine neurons tested by HPLC on day 24. DA: dopamine; DOPAC: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid; HVA: homovanillic acid. (F) DA secretion on differentiation days 0 (control), 13, 15, 18 and 24. ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n=6). (G) DOPAC secretion on differentiation days 0 (control), 13, 15, 18 and 24. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison test (n=6). Also see Figures S3-5.