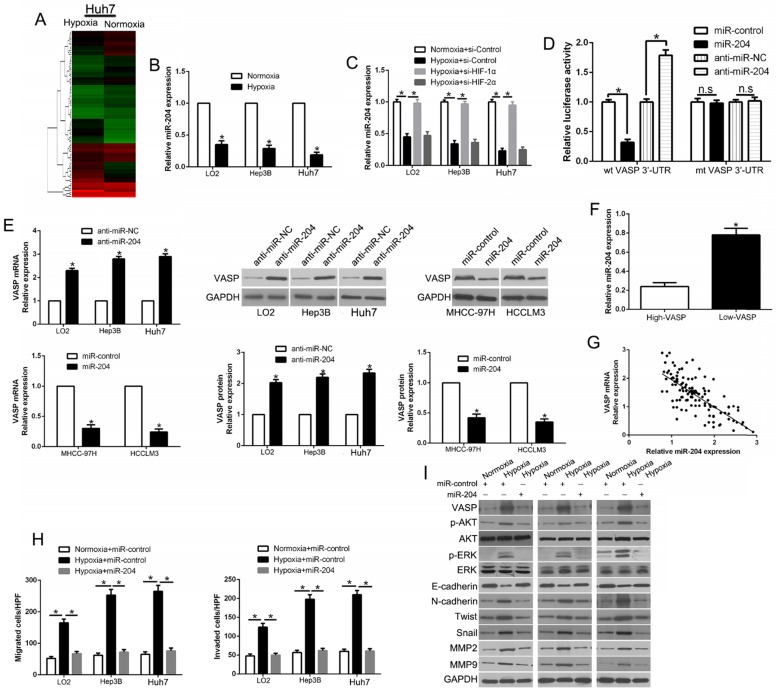
Figure 7.
Hypoxia-induced loss of miR-204 contributes to VASP up-regulation in HCC. (A) miRNA array was used to identify the differentially expressed miRNAs between Huh7 cells cultured in normoxic and hypoxic conditions. (B) qRT-PCR was performed for miR-204 in HCC cells cultured under normoxia and hypoxia. (C) qRT-PCR was performed for miR-204 in HIF-1α-knockdown LO2, Hep3B, and Huh7 cells in hypoxic condition. (D) miR-204 overexpression significantly suppressed, while miR-204 loss increased, the luciferase activity that carried wild-type (wt) but not mutant (mt) 3'-UTR of VASP. (E) LO2, Hep3B, and Huh7 cells were transfected with miR-204 inhibitors (anti-miR-204) and MHCC-97H and HCCLM3 cells were transfected with precursor miR-204 and were subjected to qRT-PCR for VASP mRNA expression. (F) The expression of miR-204 in VASP high-expressing tumors was significantly lower than that in VASP low-expressing tumors, as determined by qRT-PCR. (G) An inverse correlation between the levels of miR-204 and VASP mRNA was observed in HCC tissues. (H-I) LO2, Hep3B, and Huh7 cells cultured in normoxic or hypoxic condition were transduced with miR-204 vector and were subjected to Transwell assay for migration and invasion (H), and Western blotting (I) for EMT markers.