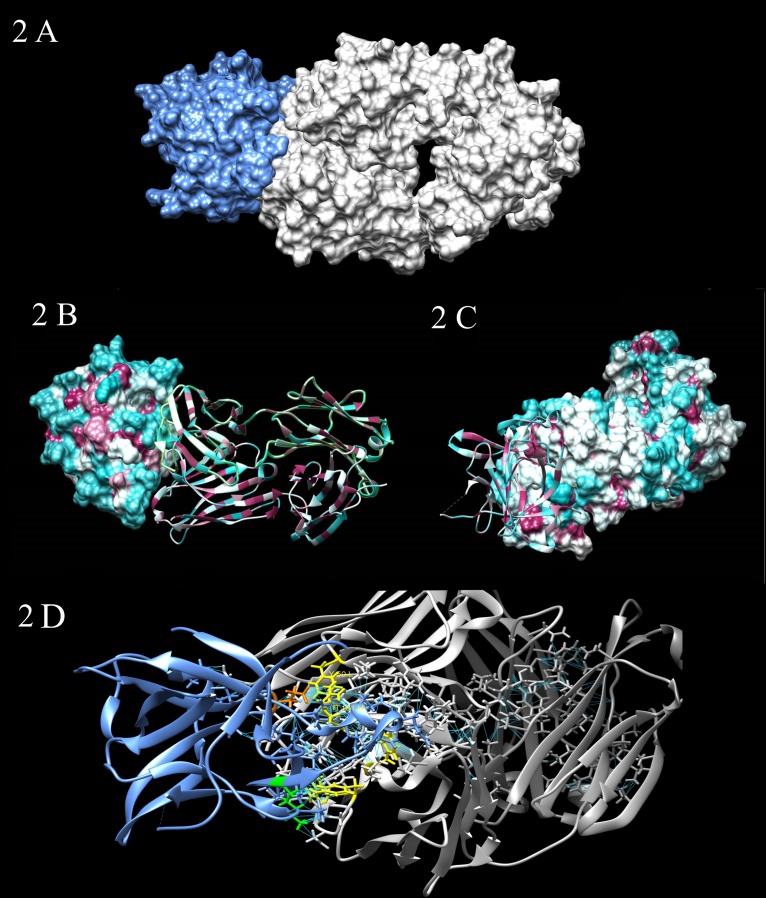
FIGURE 2.
(A) Steric complementarity between Canakinumab and IL-1β. Canakinumab (gray) binding to IL-1β (blues) largely obeys a lock-and-key type mechanism, with contributions by all CDRs and without any large structural changes of the paratope. (B,C) Hydrophobic potential of Canakinumab’s Fab heavy and light chain. The surfaces are colored according to amino acid hydrophobicity. The hydrophobic residues (larger positive values of hydrophobicity) are maroon, while the hydrophilic residues (negative values of hydrophobicity) are cyan. The binding interface is remarkably flat, extensively hydrated, and very large. The IL-1β epitope does not include any aromatic or bulky hydrophobic residues. (2 B) surface epitope; (2 C) surface paratope. (D) All kind of interactions (polar and no polar, favorable) between Canakinumab and IL-1β. The paratope residues that stand out in terms of number of intermolecular contacts to IL-1β are colored in yellow: Arginine (Arg) H101, Tryptophan (Trp) H52, Tyrosine (Tyr) H53, Tyr H32 and Tyr L50. Arg H101 of the H-CDR3 loop plays an important role by forming strong electrostatic interactions with the epitope residue Glutamic acid (Glu) 64 (orange). Lysine (Lys) 27 (green) forms salt-bridge interactions.