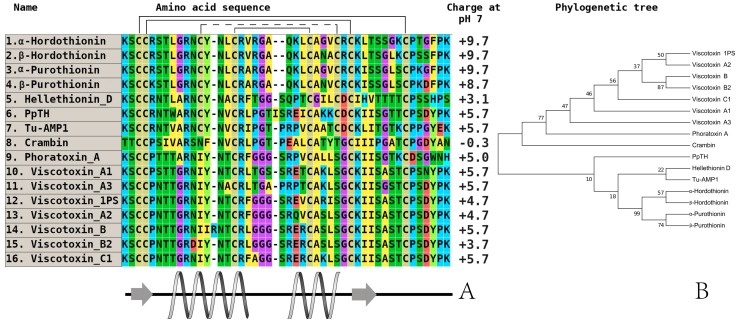
Figure 3.
The alignment (A) and phylogenetic tree (B) of plant thionins from eight and six-cysteine type subfamilies. Аmino acids are highlighted in color, and сonserved disulfide bonds are connected by black lines. Conservative elements of the secondary structure are shown under the alignment according to alpha-purothionin from soft wheat (T. aestivum), (CP) [57]. α-hordothionin—thionin from Hordeum vulgare (monocotyledons, UniProt ID: P01545), (CP); β-hordothionin—thionin from H. vulgare (UniProt ID: P21742), (CP); α-purothionin—thionin from Triticum aestivum (monocotyledons, GenBank ID: AFQ60540), (CP); β-purothionin—thionin from T. aestivum (AAB71137), (CP); hellethionin_D—thionin from Helleborus purpurascens (dicotyledons, UniProt ID: P60057), (WP); PpTH—thionin from Pyrularia pubera (dicotyledons, UniProt ID: P07504), (WP); Tu-AMP1—thionin from Tulipa gesneriana, (monocotyledons, [22]), (CP); crambin—thionin from Crambe hispanica subsp. abyssinica (dicotyledons, UniProt ID: P01542), (WP); phoratoxin_A—thionin from Phoradendron leucarpum subsp. tomentosum (dicotyledons, UniProt ID: P01539), (CP); viscotoxin_A1—thionin from Viscum album (dicotyledons, GenBank ID: 3C8P_B), (WP); viscotoxin_A3—thionin from V. album (GenBank ID: VTVAA3), (WP); viscotoxin_1PS—thionin from V. album (UniProt ID: P01537), (WP); viscotoxin_A2—thionin from V. album (UniProt ID: P32880), (WP); viscotoxin_B—thionin from V. album (UniProt ID: P08943), (WP); viscotoxin_B2—thionin from V. album (UniProt ID: P08943), (WP); viscotoxin_C1—thionin from V. album (UniProt ID: P83554), (WP). All structures are marked: CP—cultivated plant species, WP—wild plant species.