Figure 1.
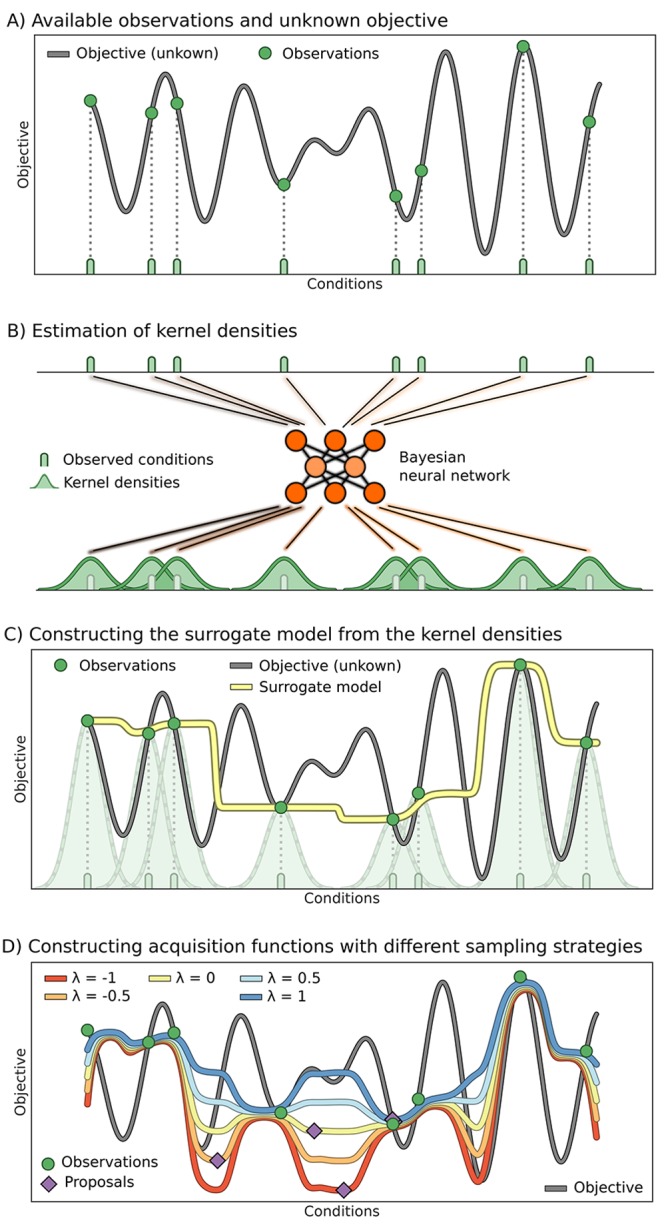
Illustration of the workflow of Phoenics. (A) Unknown, possibly high-dimensional, objective function of an experimental procedure or computation. The objective function has been evaluated at eight different conditions (green), which comprise the set of observations in this illustration. (B) The observed conditions are processed by a Bayesian neural network yielding a probabilistic model for estimating parameter kernel densities. Note that the probabilistic approach allows for a higher flexibility of our surrogate model compared to standard kernel density estimation. (C) The surrogate model is constructed by weighting the estimated parameter kernel densities with their associated observed objective values. (D) The surrogate can be globally reshaped using a single sampling parameter λ to favor exploration (red) or exploitation (blue) of the parameter space.
