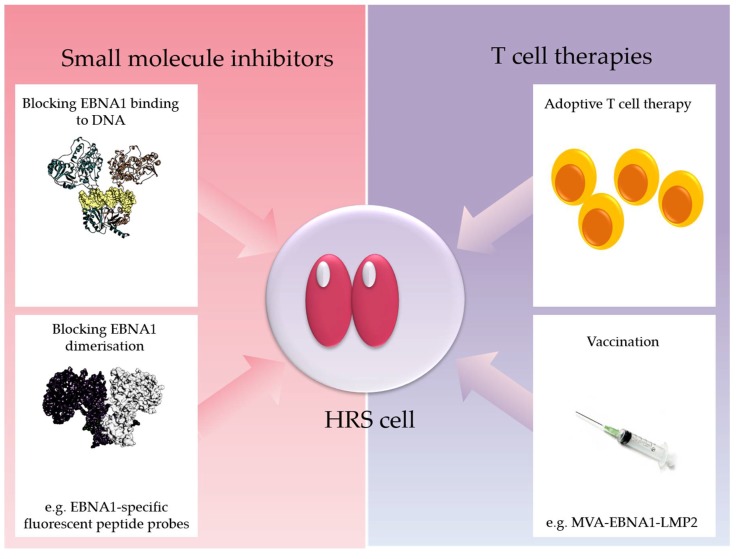
Figure 2.
EBNA1 is an emerging target for therapeutic intervention. Shown is an HRS cell expressing EBNA1. Possibilities to target EBNA1 therapeutically are indicated and include the use of small-molecule inhibitors of EBNA1, for example using drugs that block EBNA1 binding to DNA and EBNA1-specific fluorescent peptide probes which prevent EBNA1 dimerization [109,110,111], therapeutic EBV vaccines including MVA-EBNA1-LMP2 containing an EBNA1-LMP2 fusion protein [112], and adoptive T-cell therapies [113,114]. Other approaches include relieving Gar-mediated suppression of EBNA1 translation which can potentially boost EBNA1 recognition by T cells (e.g., PhenDC3) [115].