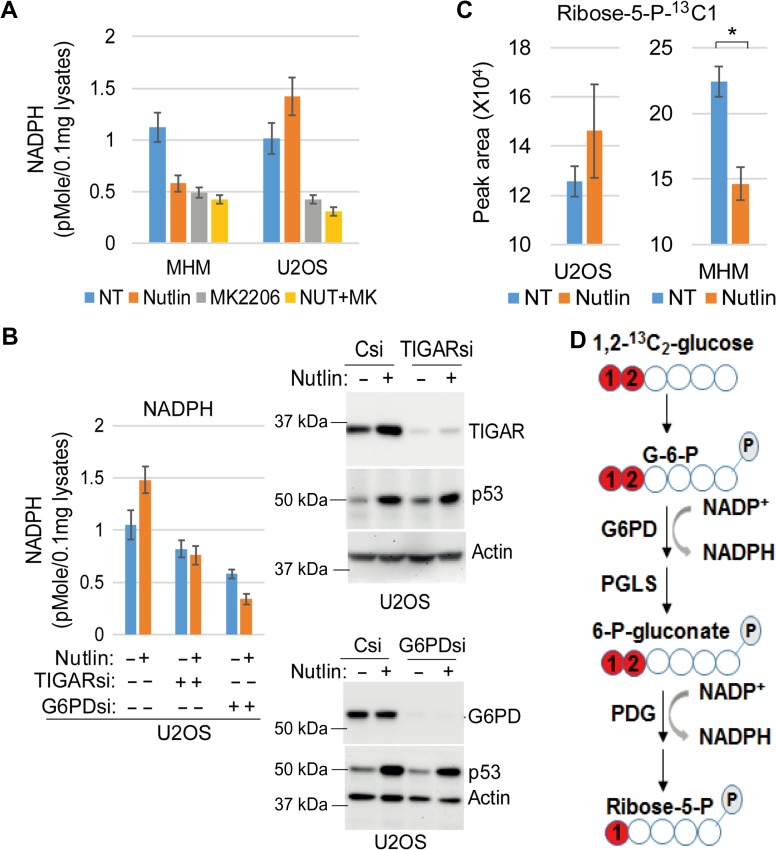
Figure 5.
Nutlin inhibits or promotes PPP. (A) Cells were treated with vehicle or Nutlin (10 μM) and/or MK2206 (10 μM) for 24 h. Lysates were analyzed for NADPH. Average NADPH level from triplicate was presented with SD indicated. (B) Cells were transfected with control siRNA, TIGAR siRNA, or G6PD siRNA and then treated with vehicle or Nutlin (10 μM) for 24 h. Lysates were analyzed for NADPH. Average NADPH level from triplicate was presented with SD indicated (left panel). Lysates were also immunoblotted for the indicated proteins (right panel). (C) cells were treated with Nutlin for a 12-h period and then fluxed with D-[1,2-13C] glucose for 15 min. Metabolites were analyzed by LC–MS. Ribose-5-P-13C1 levels in vehicle-treated and Nutlin-treated cells were presented with SD indicated. There is no significant difference between vehicle and Nutlin in U2OS cells (P = 0.22). There is significant difference between vehicle and Nutlin in MHM cells (P = 0.008). (D) Metabolism of 1,2-13C2-glucose through PPP to generate NADPH and into ribose-5-P-13C1 is schematically presented.