Figure 9.
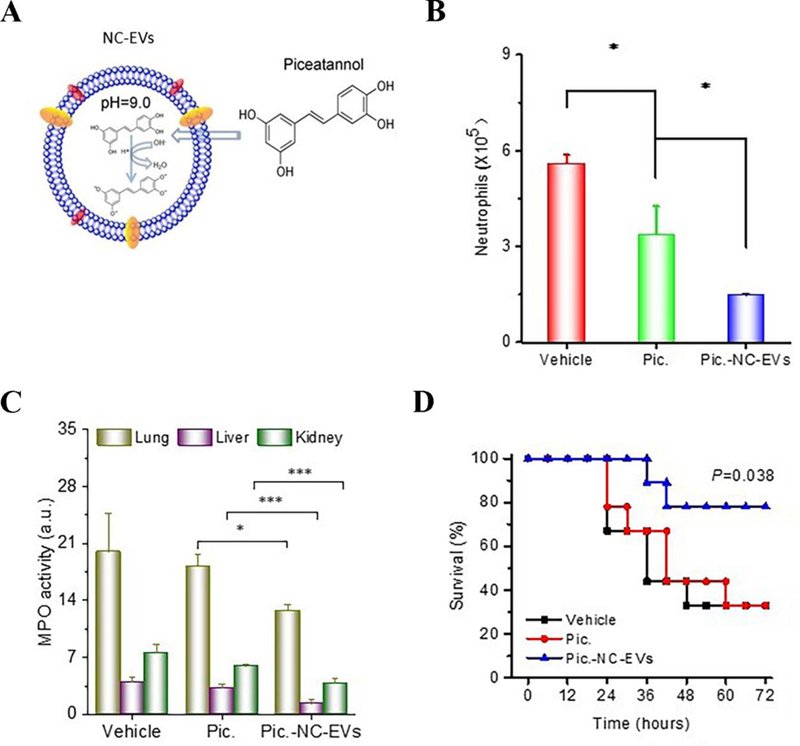
Drug-loaded neutrophil membrane vesicles for anti-inflammation therapy. (A) Schematic illustration of remote loading of piceatannol into cavitation-generated nanovesicles (NC-EVs) via pH gradient. (B) Neutrophil numbers in BALF 12 h after lung LPS challenge at a dose of 10 mg/kg. Vehicle, piceatannol (pic) (2 mg/kg) and pic-NC-EVs (pic at 2 mg/kg) were i.v. injected 2 h after LPS challenge. (C) MPO activity in mouse lung, liver and kidney 8 h after intraperitoneal (i.p.) LPS (22 mg/kg) challenge (LPS-induced sepsis model). Vehicle, piceatannol (3 mg/kg) and pic-NC-EVs (pic at 3 mg/kg) were i.v. injected 2 h after LPS challenge. The result showed that piceatannol-loaded NC-EVs decreased neutrophil tissue infiltration in all the three organs. (D) Survival rates after i.p. LPS (22 mg/kg) challenge (LPS-induced sepsis model). Vehicle, piceatannol (3 mg/kg) and pic-NC-EVs (pic at 3 mg/kg) were i.v. injected 2 h after i.p. LPS challenge. Piceatannol-loaded NC-EVs prevented death in 80% of mice. *, **, and *** represent P<0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 in two-way t-test. Copyright 2017, Elsevier.[17]
