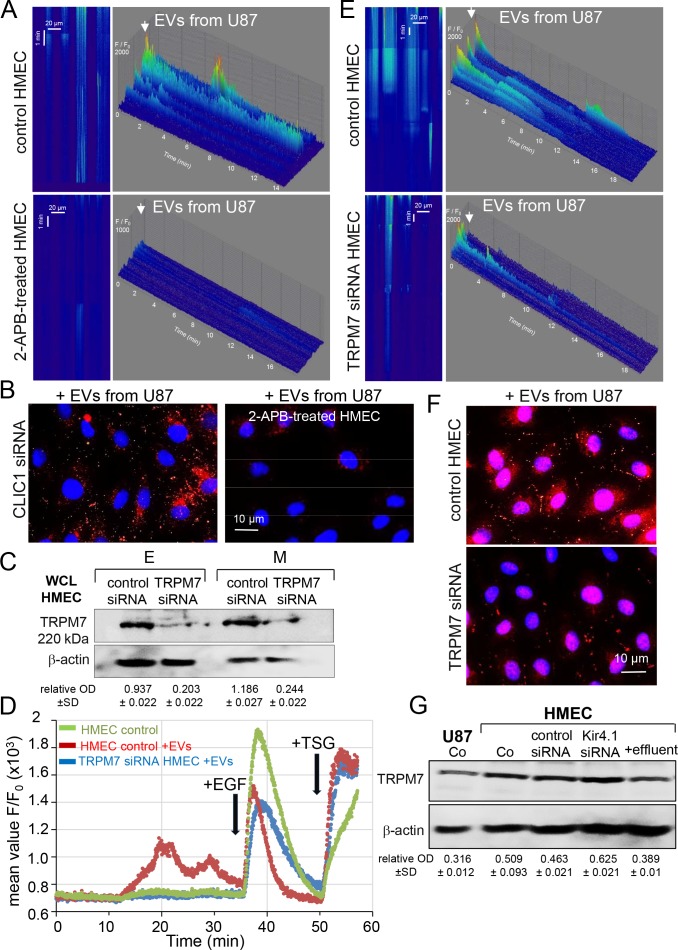
Figure 2. The vesicular transfer of CLIC1 requires cytosolic Ca2+ increases in HMEC.
(A) Line scan images of cytosolic [Ca2+] increases in Fluo-4 loaded HMEC exposed to the same amount of EVs collected from the same homotypic U87 culture. HMEC were pre-treated with 2-APB (50 μM; lower panel). Tridimensional histogram (F/F0 vs space/time) are representative of 3 experiments. (B) Transfer of vesicular CLIC1 was blocked by 2-APB (50 μM). HMEC silenced by siRNA CLIC1 were exposed to EVs from U87 (n = 3). After 24h of incubation with EVs, HMEC were stained for CLIC1 (red) and nuclei (blue). (C) Expression of TRPM7 in HMEC. Homotypic HMEC were loaded (M) or not (E) with miR-5096 upon transfection of control siRNA or siRNA targeting TRPM7. Numbers indicate mean OD values of TRPM7 related to β-actin (± SD; n = 2; 80μg proteins/lane). (D) Spatially average Ca2+ profile showing the dynamic change of Ca2+ signals with time and induced by EVs (applied at the beginning of the records) then EGF (10 ng/ml) applied at the time indicated by arrow. Cytosolic Ca2+ store depletion was performed by the addition of thapsigargin (TSG, 5μM) at the end of recordings. Values are means of fluorescent ratio F/F0 ± SD; n = 3. (E) Silencing TRPM7 in HMEC reduced the Ca2+ signal induced by EVs collected from homotypic U87 for 48h. (F) Control and silenced TRPM7 HMEC were exposed to EVs and stained for CLIC1 (red) after 24 h of culture (representative of 3 experiments). (G) Expression of TRPM7 in homotypic HMEC upon transfection of control siRNA or siRNA targeting Kir4.1 [18]. HMEC were exposed to the effluent (soluble fraction) from homotypic U87. Numbers indicate mean OD values of TRPM7 related to β-actin (± SD; n = 2).