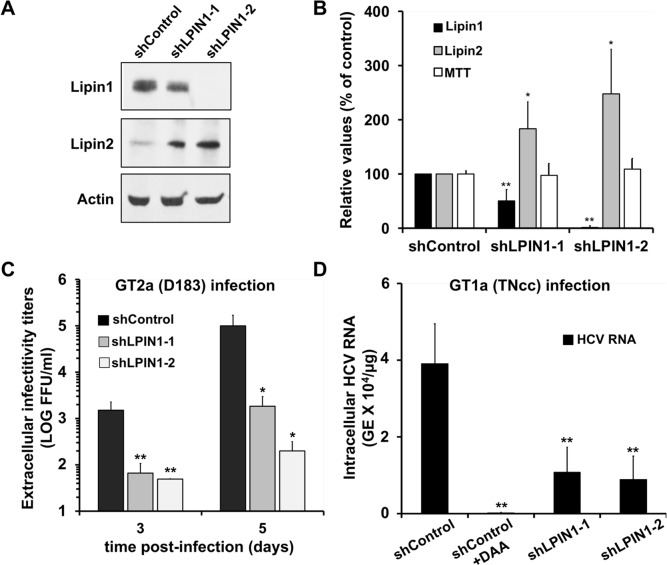
Fig 2. HCV propagation is limited in lipin1-deficient cells.
Huh-7 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing control or LPIN1-specific shRNAs. Seven days after transduction samples of the cells were collected for Western-blot analysis using antibodies against lipin1 and lipin2 and actin as loading control. Parallel cultures were subjected to an MTT assay to determine their viability as described in the methods section. (A) Representative Western-Blot showing cellular lipin1 and lipin2 protein expression levels and a loading control (actin). (B) Average expression values for lipin1 and lipin2 as determined by Western-Blot and cell viability as determined by an MTT assay. Data are shown as average and SD of six independent transduction experiments (n = 6). (C) Huh-7 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing control or LPIN1-specific shRNAs. At day 3 post-transduction, cells were infected at MOI 0.01 with HCV D183 virus. Samples of cell supernatants were collected at days 3 and 5 post-infection to determine the extracellular infectivity titer. Average and SD of the infectivity titers at day 3 and 5 of two independent infections performed in triplicate (n = 6). (D) Huh-7.5 cells were transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing control or LPIN1-specific shRNAs. Silenced cells were infected 7 days after transduction at MOI 0.05 with genotype 1a HCV (TNcc) in the presence or absence of 2mAde (10μM; shControl+DAA). Intracellular HCV RNA was determined by RT-qPCR 72 hours post-infection. Data are shown as average and SD of three experiments performed in triplicate (n = 9). Statistical significance was determined using Student´s t-test (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).