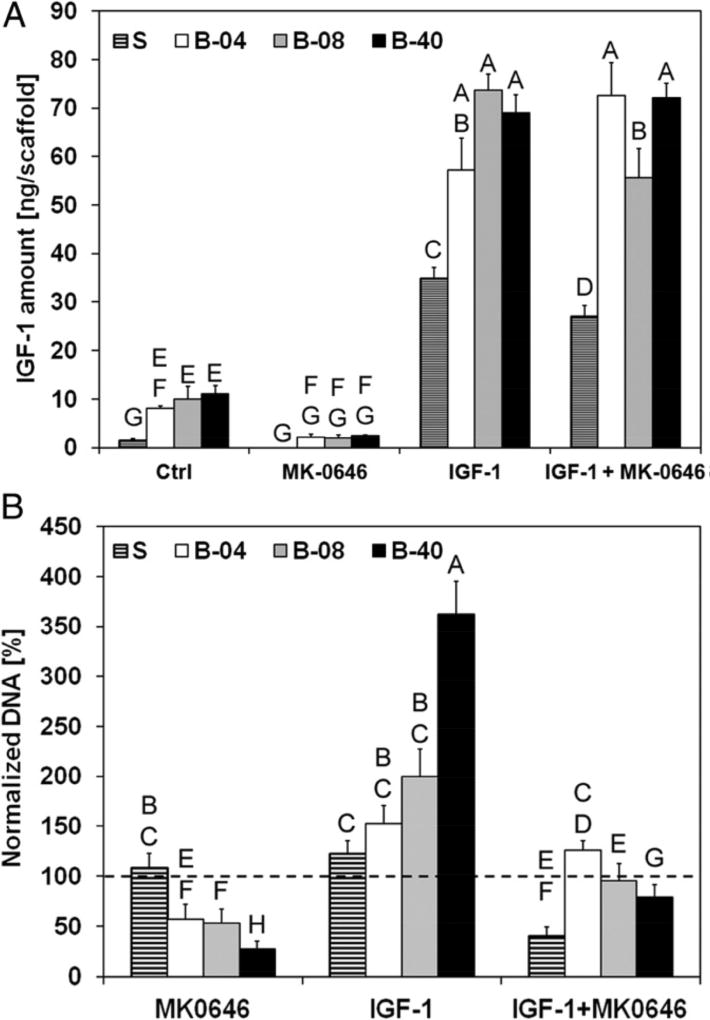
Figure 2.
Effect of flow-derived shear stress on Ewing sarcoma cell sensitivity to dalotuzumab (MK-0646), a humanized monoclonal antibody inhibitor of human IGF-1R. Santoro et al. measured IGF-1 ligand secretion and drug sensitivity in ES cells cultured under static (S) conditions or different flow rates in a bioreactor (B-04, 0.04 mL/min; B-08, 0.08 mL/min; B-40, 0.40 mL/min) [37]. (A) IGF-1 per scaffold in conditioned media after 10 days of culture. Culture of ES cells in flow conditions stimulates autocrine IGF-1 secretion. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (B) ES cell viability after 3 days of culture followed by 7 days of exposure to dalotuzumab, IGF-1, or both. Cell viability is presented as the DNA content of the treatment group normalized to the DNA content of the untreated group. Dotted line represents 100% baseline. Higher shear stress leads to resistance to dalotuzumab activity and competitive binding between IGF-1 and dalotuzumab favors IGF-1, but convective transport under high flow rate increases availability of the drug to cells. Error bars represent SD (n = 6). Levels not connected by the same letter are statistically different (P < 0.05). Image used with permission from the authors as required for images included in articles published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA.