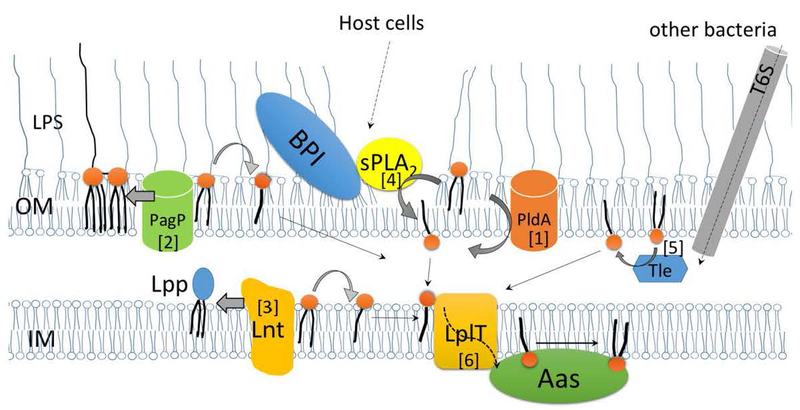
Fig. 1. Routes of lysophospholipid biogenesis and remodeling in the Gram-negative bacterial envelope.
Lysophospholipids are generated in the periplasm. In the OM, [1] activated PldA hydrolyzes a PE to generate LPE; [2] PagP catalyzes the transfer of a palmitoyl group from a PE to lipid A, generating hepta-acylated lipid A and LPE as by-product. In the IM, [3] Lnt transfers the fatty acid moiety from PE to the N terminus of a major outer membrane lipoprotein precursor (Lpp), generating a triacylated mature Lpp and releasing LPE as by-product. LPL can be generated by membrane degradation mediated by [4] exogenous sPLA2 and BPI from the host or by [5] the Tle protein delivered from invading bacteria via the type VI secretion system (T6S). The generated LPLs are translocated by LplT [6] from the outer leaflet to the inner leaflet of the IM where they can be reacylated by the coupled acyltransferase Aas.