Figure 5. Local blockade of type-1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1R) in the lateral habenula (LHb) decreases anxiety-like behavior.
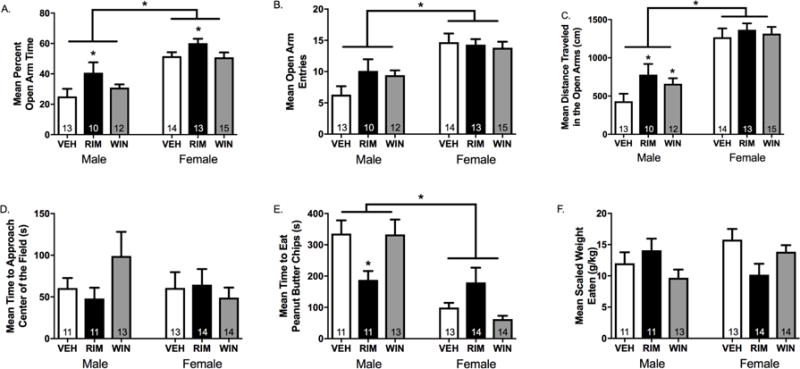
Rats received an intra-LHb infusion of the CB1R agonist WIN 55212-2 (WIN), the CB1R antagonist rimonabant (RIM), or vehicle (VEH) 15 min prior testing in either the elevated plus maze (EPM) or novelty-suppressed feeding test (NSFT). (A) With respect to the percentage of time spent exploring the open arms of the EPM, there was a main effect of treatment (F2,86=3.98, p=0.03, ηp2=0.14), a main effect of sex (F1,86=41.89, p<0.001, ηp2=0.45), but no treatment × sex interaction (F2,86=0.53, p=0.59, ηp2=0.02). Post-hoc analyses revealed that intra-LHb RIM administration significantly increased the percentage of time spent exploring the open arms in male (t20=−2.26, p=0.04, d=0.96) and female (t24=−2.24, p=0.04, d=1.0) rats compared to VEH. (B) There was no effect of treatment on the total number of open arm entries (F2,86=2.69, p=0.08, ηp2=0.10), a main effect of sex (F1,86=19.80, p<0.001, ηp2=0.28), and no significant interaction treatment × sex interaction (F2,86=0.24, p=0.79, ηp2=0.01). (C) There was a main effect of treatment on the total distance travelled in the open arms of the EPM (F2,86=4.17, p=0.02, ηp2=0.14), a main effect of sex (F1,86=33.17, p<0.001, ηp2 =0.39), and no significant treatment × sex interaction (F2,86=0.31, p=0.74, ηp2=0.01). Post-hoc analyses revealed that, in male rats, the total distance travelled in the open arms was significantly increased following intra-LHb RIM (t20=−2.45, p=0.02, d=1.03) or WIN (t22=−2.55, p=0.02, d=1.04) treatment compared to VEH. In female rats, there was no effect of RIM (t25=−1.73, p=0.11, d=0.93) or WIN (t13=−1.89, p=0.08, d=0.99) on distance travelled in the open arms. (D) In the NSFT, there was no effect of treatment (F2,86=0.15, p=0.86, ηp2=0.01), sex (F1, 86=0.20, p=0.66, ηp2<0.01), or treatment × sex interaction (F2,86=1.39, p=0.26, ηp2=0.05) on the latency to approach the peanut butter chips. (E) However, with respect to the latency to consume the peanut butter chips, there was a main effect of treatment (F2,86=0.02, p=0.98, ηp2<0.01), sex (F1,86=28.35, p<0.001, ηp2=0.26), and a significant treatment × sex interaction (F3,86=5.06, p=0.003, ηp2=0.16). Post-hoc analyses revealed that intra-LHb RIM administration significantly decreased the latency to consume the peanut butter chips compared to VEH in male (t20=3.25, p=0.004, d=1.39), but not female (t25=−1.46, p=0.16, d=0.58) rats. (F) There was no effect of treatment (F2,86=0.64, p=0.53, ηp2=0.05), sex (F2,86=0.79, p=0.38, ηp2=0.02), or treatment × sex interaction (F2,86=1.80, p=0.18, ηp2=0.07) with respect to the weight of peanut butter chips consumed in the home cage after the test, thus indicating that the effects observed were not due to treatment-induced hyperphagia. n=10-15/group/sex; * denotes significance at p<0.05.
