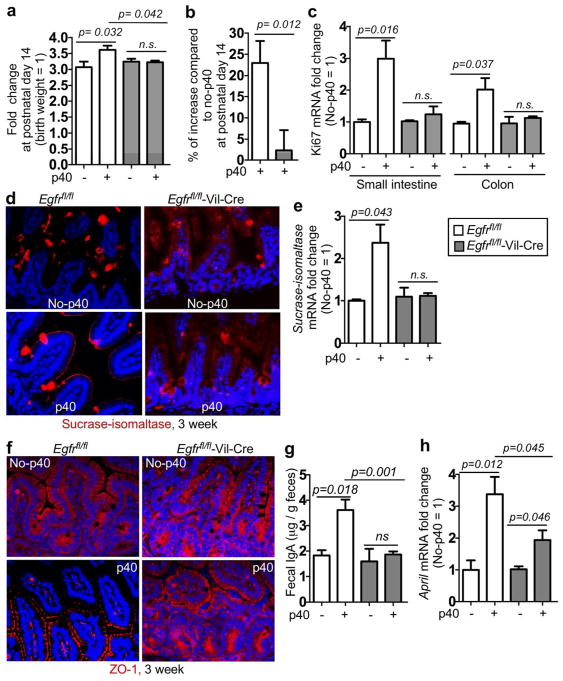
Figure 6. EGFR expression in intestinal epithelial cells mediates developmental effects of p40 in pups.
Egfrfl/fl and Egfrfl/fl-Vil-Cre pups were treated with p40 as described in Figure 2. (A) The fold change of bodyweight (a) and the percentage of bodyweight increase (b) at postnatal day 14 were calculated as described in Figure 2. (c) Real-time PCR analysis was performed to detect Ki67 gene expression in the small intestine and the colon of 2-week old mice. (d–e) The ileum tissues from 3-week old mice were prepared for sucrose-isomaltase immunostaining and Real-time PCR analysis to detect gene expression. (f) The colonic tissues from 3-week old mice were prepared for ZO-1 immunostaining. (g) Feces from 2-week old mice were collected for ELISA to detect fecal IgA levels. (h) Real-time PCR analysis was performed to detect APRIL gene expression in the small intestine of 2-week old mice. In c and h: the average of mRNA expression levels in the no-p40 group were set as 100%, and the mRNA expression level of each mouse was compared to the average. In a–c, e, and f–h, n= 5–9 in each group. In d and f, no-p40: n=3–5, p40: n=5–7 in each group.