Figure 1.
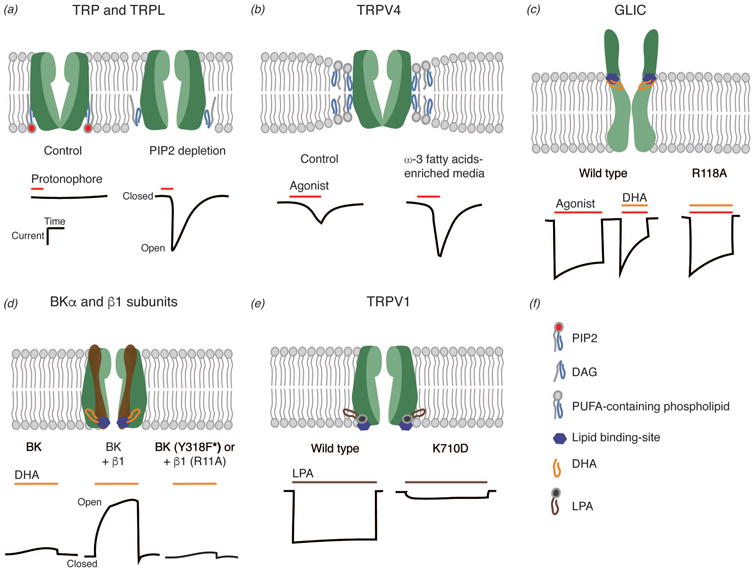
Mechanisms underlying ion channel regulation by lipids. (a) Light-sensitive TRP and TRP-like(L) channels. (b) Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 (TRPV4). (c) Prokaryotic pentameric ligand-gated ion channel from the cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus (GLIC). (d) Ca2+-activated large-conductance K+ (BK) channel (α) and auxiliary subunit (β1). F*: phenylalanine-based unnatural amino acid residue. (e) Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1). (f) Schematic representation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), diacylglycerol (DAG), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)-containing phospholipids, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).
