Fig. 1.
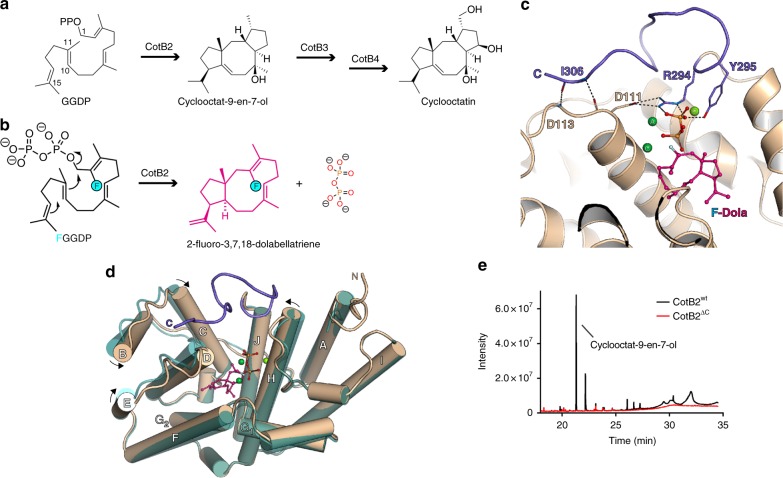
Enzymatic reaction and the structure of the closed state of CotB2, revealing the importance of its C-terminus. a The linear substrate geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGDP) is cyclised by CotB2 to a fusicoccane, with a 5-8-5 fused ring system, which is subsequently elaborated to the bioactive compound cyclooctatin by two cytochrome P450 enzymes CotB3 and CotB4, respectively. b 2-fluorogeranylgeranyl diphosphate (FGGDP) is converted to 2-fluoro-3,17,18-dolabellatriene (F-Dola). The fluorinated position of the substrate-analogue FGGPP is indicated by a light blue circle. c View into the active site of CotB2wt•Mg2+3•F-Dola. CotB2 is shown in cartoon representation coloured in light brown. The bound intermediate is shown in magenta and Mg2+-ions are shown in green. Folding of the C-terminus (purple) leads to the formation of several hydrogen bonds (dashed lines), allowing for sensing of the different catalytically important motives. d Structural superposition of CotB2wt (open), shown in teal, and CotB2•Mg2+3•F-Dola (closed), shown in light brown. e GC/MS spectrum to monitor product formation by CotB2wt (black) and CotB2ΔC (red). Deletion of the C-terminus results in an inactive enzyme