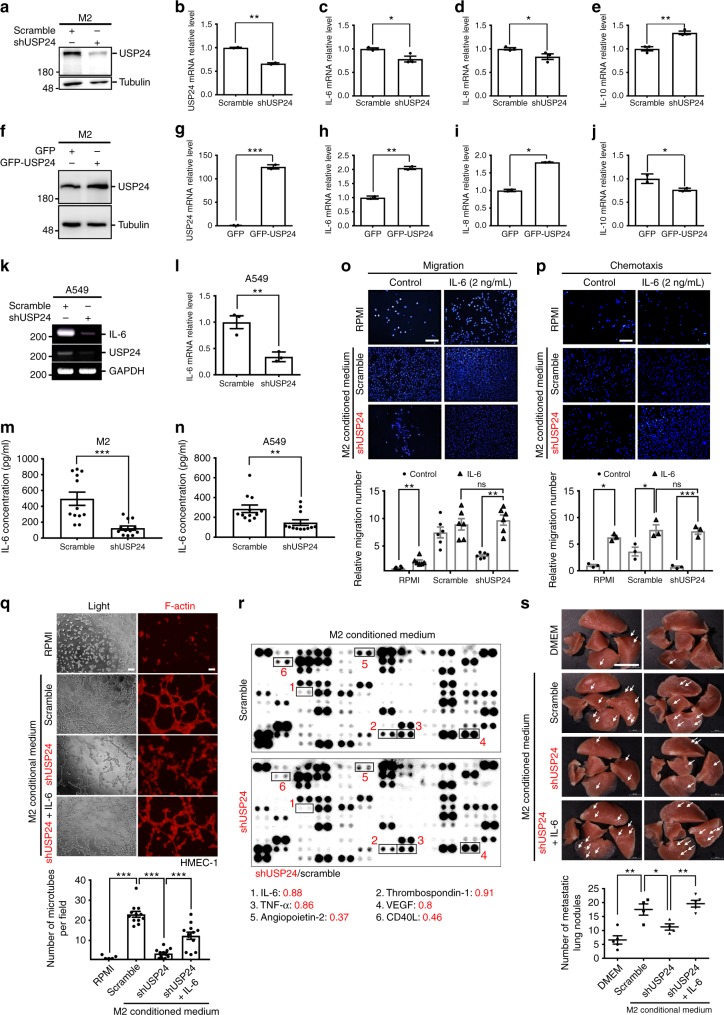
Fig. 3.
IL-6 regulated by USP24 increases lung cancer metastasis. a–j Western blot and Q-PCR was utilized to analyze the protein level of USP24 (a, f) and mRNA levels of USP24, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 in M2 macrophages after USP24 knockdown (b–e) or overexpression (g–j) (n = 3). k, l IL-6 mRNA level in A549 cells was analyzed by RT-PCR (k) and Q-PCR (l) after USP24 knockdown (n = 3). Results of Q-PCR were normalized with GAPDH and expressed as fold of control. m, n IL-6 secretion was analyzed in conditioned medium derived from M2 macrophages (m) and A549 cells (n) after USP24 knockdown (n = 12). o–q IL-6 was replenished in USP24-knockdown M2 macrophages derived conditioned medium, and migration assay (o) (n = 6), chemotaxis assay (p) (n = 3) (DAPI staining, scale bar: 100 μm), and angiogenesis assay (q) (n = 12) (scale bar: 200 μm.) were analyzed. Results were normalized with control and expressed as fold of control. r The levels of IL-6, Thrombospondin-1, TNF-α, VEGF, Angiopoietin-2 and CD40L were studied by using protein array. s CL1–5 cells were treated with DMEM (n = 5) or conditioned medium derived from scramble knockdown (n = 4), USP24 knockdown (n = 4) or IL-6 replenished USP24 knockdown (n = 5) M2 macrophages for 24 h and injected into SCID mice through tail vein injection. The white arrowheads indicate the metastatic nodules (scale bar: 1 cm). Data are shown as mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test, ns for not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005