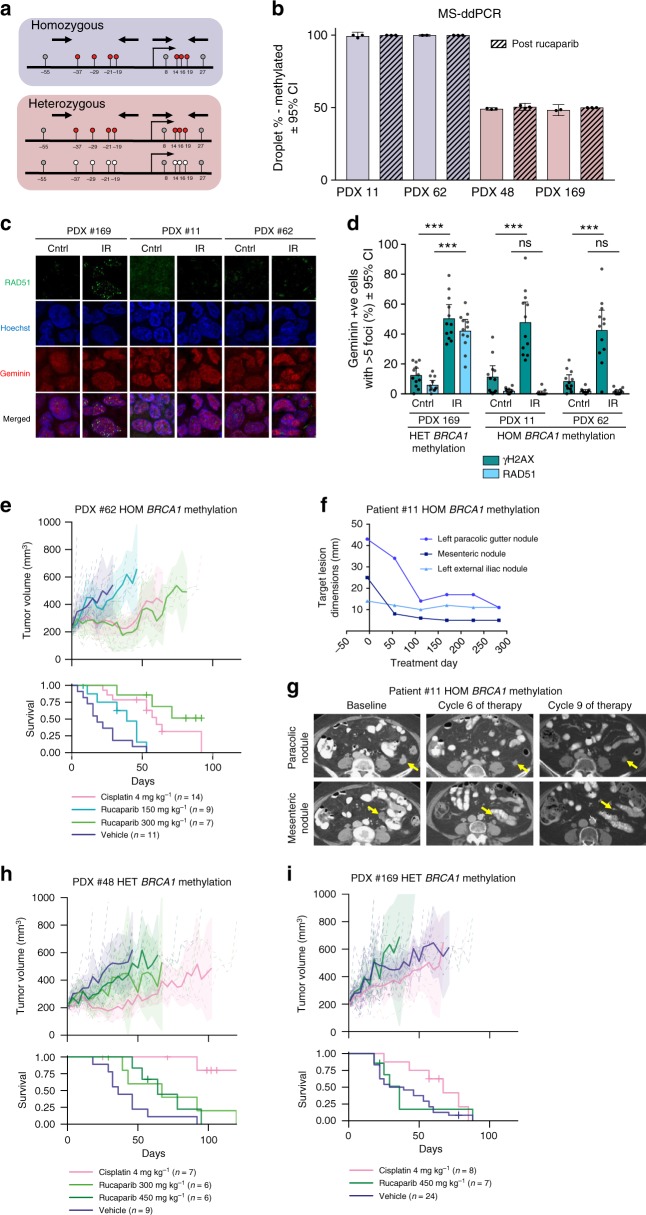
Fig. 3.
BRCA1 promoter methylation in HGSOC PDX and rucaparib response. a A diagram of two modes of BRCA1 promoter methylation observed in four PDX #11, #62, #48, and #169. Homozygous methylation status was assigned when % of methylation was close to 100%, therefore all observed copies were methylated. Heterozygous methylation status was assigned when both, methylated and unmethylated, copies were observed. b BRCA1 methylation in four HGSOC PDX (#62, #48, #169, #11) assessed by MS-ddPCR (mean ± 95% CI); n = 2–3 mice for each treatment and PDX model. c RAD51 foci formation 4 h after 10 Gy irradiation was observed in PDX #169 with heterozygous BRCA1 methylation and not in PDX #11 and PDX #62 with homozygous BRCA1 methylation. d Quantification of ex vivo γH2AX and RAD51 foci formation in geminin-positive cells 4 h after 10 Gy irradiation (mean ± 95% CI). γH2AX foci are observed at the sites of DNA damage, and RAD51 foci are observed at the sites of HR pathway repair; n = 12 (four fields of view from three independent experiments) for each treatment and PDX model. Untreated and irradiated cells were compared by multiple t-tests for γH2AX and RAD51 foci formation. ***p < 0.001; ns not significant. e Responses to cisplatin and rucaparib in vivo treatment observed in chemo-naive PDX #62 with homozygous BRCA1 methylation. f RECIST 1.1 measurements of three monitored tumor lesions in patient #11, with homozygous methylation of BRCA1, treated with rucaparib. g CT scans of the two largest monitored lesions prior to and during rucaparib treatment of the patient #11. h, i Responses to cisplatin and rucaparib in vivo treatment observed in PDX #48 and #169 with heterozygous BRCA1 methylation. Recipient mice bearing PDX were randomized to treatment with vehicle or rucaparib, at the dose shown. PDX were harvested at a tumor volume of 600–700 mm3 (see Table 1 and Supplementary Data 2 for median TTH and p-values for survival comparison). Mean tumor volume (mm3) ± 95% CI (hashed lines are representing individual mice) and corresponding Kaplan–Meier survival analysis. Censored events are represented by crosses on Kaplan–Meier plot; n = individual mice. HOM homozygous, HET heterozygous